More accurately these tools calculate the second moment of area which is a purely geometric property of a planar shape not related to its mass. This tool calculates the moment of inertia I second moment of area of an angle.

Segment the beam section into partsWhen calculating the area moment of inertia we must calculate the moment of.
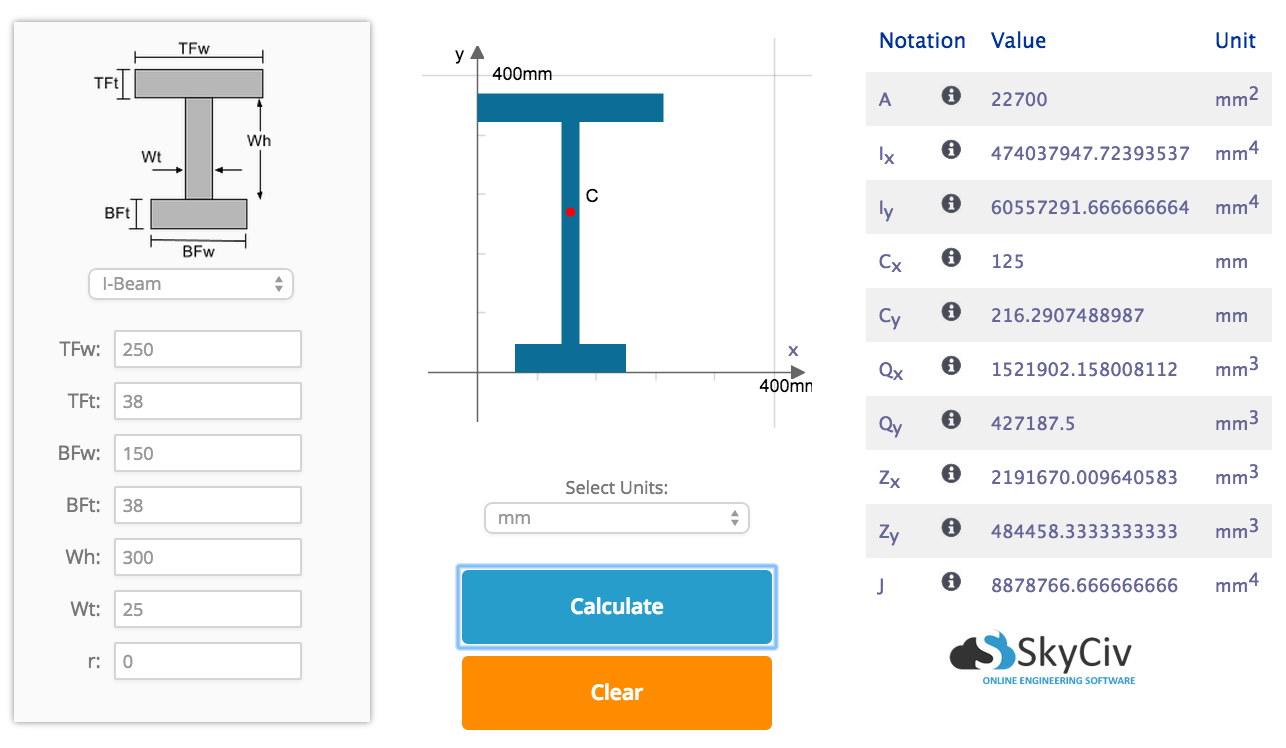
Calculate moment of inertia. It allows you to. Calculate the Moment of Inertia I of a beam section Second Moment of Area Centroid Calculator used to calculate the Centroid C in the X and Y axis of a beam section Calculate the First moment of area Statical Moment of Inertia Q of a beam section First Moment of Area A. For instance for a golf ball youre whirling around on a string the moment of inertia depends on the radius of the circle the ball is spinning in.
Here r is the radius of the circle from the center of rotation to the point at which all the mass of the golf ball is concentrated. Here are the steps for you to follow. First select the Shape from the drop-down menu.
The choices are Triangle Rectangle Semi-circle Circle Ellipse and. Then enter the value of the Base and choose the unit of measurement from the drop-down menu. Finally enter the value of the Height and.
For non-uniform objects moment of inertia is calculated by the sum of the products of individual point masses and their corresponding distance from the axis of rotation. This generalized relationship can be used to calculate the moment of inertia of any system since any object can be constituted as an aggregation of similar point masses. Calculating Moments of Inertia Calculate themoment of inertiafor uniformly shaped rigid bodies Apply theparallel axistheorem to find themoment of inertiaabout any axis parallel to one already known Calculate themoment of inertiafor compound objects.
Basically for any rotating object the moment of inertia can be calculated by taking the distance of each particle from the axis of rotation r in the equation squaring that value thats the r2 term and multiplying it times the mass of that particle. But for now lets look at a step-by-step guide and example of how to calculate moment of inertia. Segment the beam section into partsWhen calculating the area moment of inertia we must calculate the moment of.
Calculate the Neutral Axis NAThe Neutral Axis NA or the. The Moment of Inertia with respect to rotation around the z-axis of a single mass of 1 kg distributed as a thin ring as indicated in the figure above can be calculated as Iz 1 kg 1000 mm 0001 mmm2 1 kg m2 Moment of Inertia - Distributed Masses. To calculate the moment of inertia of a compound shape successfully you must memorize the basic formula of the moment of inertia of basic geometric elements.
These formulas are only applicable if the centroid of a basic shape coincides with the centroid of the irregular shape. Moment of Inertia and Radius of Gyration of Basic Shapes. T Section Area Moment of Inertia Formula.
Area moment of inertia. I xx bHy c-H2 2 bH 3 12 hBH h2 - y c 2 h 3 B12. Area moment of inertia.
I yy b 3 H12 B 3 h12. X c B2. Y c Hh2hBH 2 b2A.
This tool calculates the moment of inertia I second moment of area of an angle. Enter the shape dimensions b h and t below. The calculated results will have the same units as your input.
Please use consistent units for any input. Moment of Inertia General Form. Since the moment of inertia of an ordinary object involves a continuous distribution of mass at a continually varying distance from any rotation axis the calculation of moments of inertia generally involves calculus the discipline of mathematics which can handle such continuous variables.
The Product Moment of Inertia is by definition zero for principal axes. The elastic section moduli are equal to the second moments of area moments of inertia divided by the distance to the farthest fibre in the cross-section perpendicular to the axis of bending. More accurately these tools calculate the second moment of area which is a purely geometric property of a planar shape not related to its mass.
The second moment of area is commonly used in engineering disciplines where by custom is called moment of inertia. Moment of inertia may be expressed in units of kilogram metre squared kgm 2 in SI units and pound-foot-second squared lbffts 2 in imperial or US units. Moment of inertia plays the role in rotational kinetics that mass inertia plays in linear kineticsboth characterize the resistance of a body to changes in its motion.
The moment of inertia depends on how mass is distributed around an axis of rotation and will vary depending on the chosen axis. The first step to calculate moment of inertia for a mass is to establish the location of the X Y and Z axes. The accuracy of the calculations and later on the accuracy of the measurements to verify the calculations will depend entirely on the wisdom used in choosing the axes.
The key to calculating the moment of inertia for a rigid body is learning to use and apply the appropriate equations. Consider the pencil from the previous section being spun end-over-end around a central point along its length. Use this beam span calculator to determine the reactions at the supports draw the shear and moment diagram for the beam and calculate the deflection of a steel or wood beam.
Free online beam calculator for generating the reactions calculating the deflection of a steel or wood beam drawing the shear and moment diagrams for the beam.