The moving parts of your heart are all classified as mechanical. In the atrial diastole period.

The remaining 07 seconds the atria relaxes and receives venous return from the venacavae.
Cardiac cycle for dummies. It beats continually every 08 seconds of your life. The eight-tenths of a second that a heart beats is called the cardiac cycle. During that 08-second period your heart forces blood into your blood vessels for 04 seconds and then takes a quick rest for just 04 seconds.
Heres what happens in those 08 seconds. The cardiac cycle has 3 stages. Atrial and Ventricular diastole chambers are relaxed and filling with blood Atrial systole atria contract and remaining blood is pushed into ventricles Ventricular systole ventricles contract and push blood out through aorta and pulmonary artery.
The Cardiac Cycle The stages of the cardiac cycle can be roughly divided into four stages. Filling phase the ventricles fill during diastole and atrial systole. Isovolumetric contraction the ventricles contract building up pressure ready to pump blood into the aortapulmonary trunk.
Cardiac Cycle Phases 01. During the ventricular diastole period the atria and heart ventricles are relaxed and the atrioventricular valves. At the beginning of the ventricular systole period the right ventricle which is filled with blood passed on from.
In the atrial diastole period. The period of time that begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle. The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole.
The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and diastole and it is essential that these components be carefully regulated and coordinated to ensure blood is pumped. The duration of 1 cardiac cycle is 08 seconds.
The cycles are different in the atria and the ventricles. Atrial systole makes up only 01 second and is responsible for active ventricular filling. The remaining 07 seconds the atria relaxes and receives venous return from the venacavae.
This cycle is the sequence of events that occur when the heart beats. During the diastole phase of the cardiac cycle the atria and ventricles are relaxed and blood flows into the atria and ventricles. In the systole phase the ventricles contract sending blood to the rest of the body.
Two Equally Important Cardiac Systems It is easiest to think of the heart as having two separate but equally important systems. Similar to a car engine however in this analogy your cars battery is built into the engine and gasoline is actually blood. The moving parts of your heart are all classified as mechanical.
To achieve this the pacemaker has two functions PACE or INHIBIT. Lets take a pacemaker with a single ventricular lead and run through a cardiac cycle. A ventricular contraction is sensed by the pacemaker.
This begins the RR delay in this case 1 second to correspond to 60 beats per minute. Cardiac cycle For understanding ECG we first need to understand the cardiac cycle and we have already discussed in detail each and every step of the cardiac cycle. But broadly cardiac cycle passes through two major phases.
Phases of the cardiac cycle. This video is available for instant download licensing here. The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur and repeat with every heartbeat.
It can be divided into 2 major phases. SYSTOLE and DIASTOLE each of which SUBdivides into several smaller phases. Systole and diastole when not specified otherwise refer to VENTRICULAR contraction and relaxation respectively.
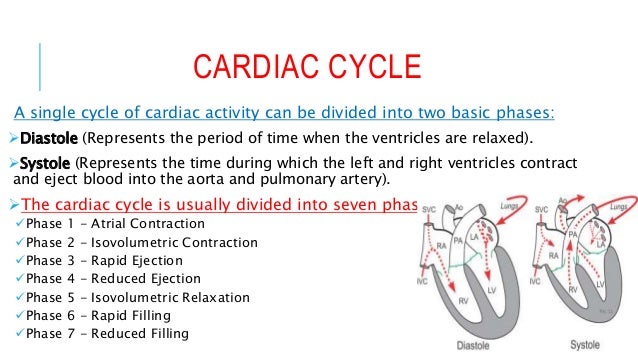
To analyze systole and diastole in more detail the cardiac cycle is usually divided into seven phases. The first phase begins with the P wave of the electrocardiogram which represents atrial depolarization and is the last phase of diastole. Phases 2-4 represent systole and phases 5-7 represent early and mid-diastole.
The cardiac cycle sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats involves a lot of different things allowing the heart to work. The different phases of the cardiac cycle are described by changes of pressure and volume of the left ventricle during diastole also known as the filling stage. The cardiac cycle is the series of contractions in the heart that pressurize different chambers causing blood to flood in one direction.
There are two stages during the cardiac cycle. During diastole the ventricles relax and fill with blood. The muscles contract during systole pushing blood through the arteries.
What I just described is one cardiac cycle or the sequence of events in a single heartbeat. Since the average heart beats about 75 beats per minute the length of each cardiac cycle is less than. Most Echo capable machines allow on screen ECG to aid with interpretation of the cardiac cycle.
The Sonosite Machine with ECG monitoring. Further reading on Basic USS and Echo can be found here. ACEM College Basic Ultrasound PDF.
Cardiology Explained Echo.