For example in NO 3 the nitrogen is assigned an oxidation number of 5 and each oxygen an oxidation number of 2. By definition the oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom would have if the compound was composed of ions.

Assign any lone pairs to the atom they are located on.
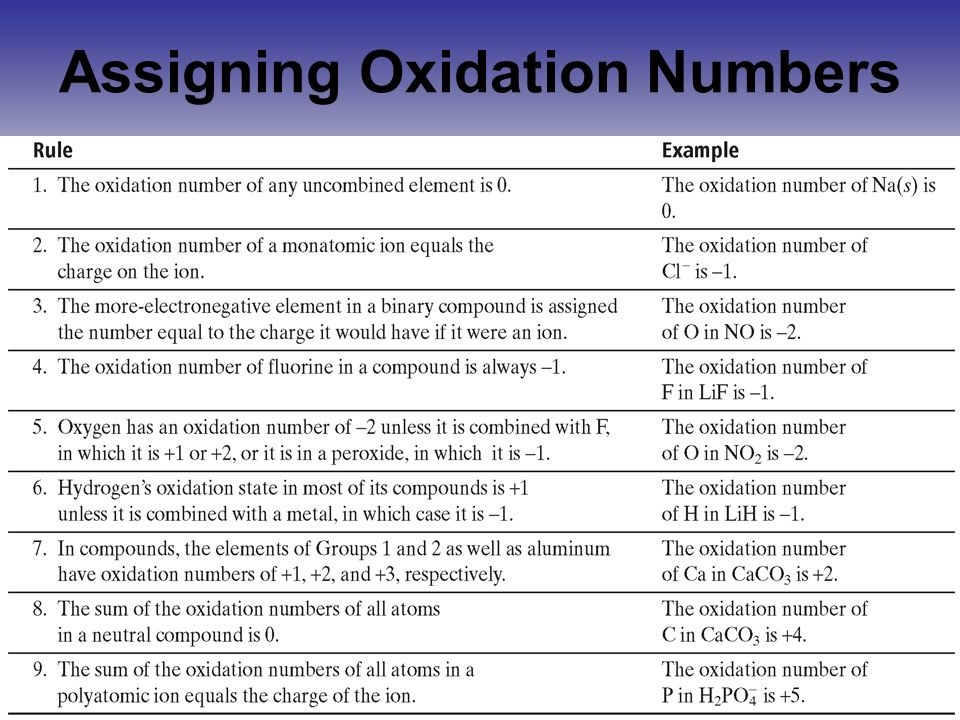
How do you assign oxidation numbers. Oxidation numbers are assigned to elements using these rules. The oxidation number of an element in its free uncombined state is zero for example Al s or Zn s. This is also true for elements found in nature as diatomic two-atom elements.
And for sulfur found as. Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The convention is that the cation is written first in a formula followed by the anion. For example in NaH the H is.
The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. The atoms in He and N 2 for example have oxidation numbers of 0. The oxidation number.
2261 1 Mn 4 2 0 2262 Mn 7 0 2263 Mn 7. When dealing with oxidation numbers we must always include the charge on the atom. Another way to determine the oxidation number of Mn in this compound is to recall that the permanganate anion MnO 4 has a charge of 1.
Summary Oxidation state shows the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element a positive oxidation state or added to an element a negative oxidation state to get to its present state. Oxidation involves an increase in oxidation state Reduction involves a decrease in oxidation state. Oxidation numbers are used to track how many electrons are lost or gained in a chemical reactions.
Assigning these numbers involves several rules. Free atoms H2 usually have an oxidation number of 0 monoatomic ions Cl- are usually equal to their charge and polyatomic ions have several governing principles. Assigning Oxidation Numbers Based on Chemical Rules 1.
Determine whether the substance in question is elemental. Free uncombined elemental atoms always have an oxidation. Determine whether the substance in question is an ion.
Ions have oxidation numbers equal to their charge. This is done by assigning oxidation numbers to each atom before and after the reaction. For example in NO 3 the nitrogen is assigned an oxidation number of 5 and each oxygen an oxidation number of 2.
This arbitrary assignment corresponds to the nitrogens having lost its original five valence electrons to the electronegative oxygens. The oxidation number of an atom simply shows the number of electrons it can account for in a redox reaction or the degree to which it has undergone oxidation. A redox reaction one of the most fundamental and commonly seen principles of chemistry is a reaction where electrons are transferred between two atomsmolecules.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. Fluorine in compounds is always assigned an oxidation number of -1.
The alkali metals group I always have an oxidation number of 1. The oxidation numbers tell us how electrons. Well learn how to determine the oxidation numbers or oxidation states for a the elements in a chemical compound.
To help identify these less obvious redox reactions chemists have developed the concept of oxidation numbers which provides a way to track electrons before and after a reaction. An atoms oxidation number or oxidation state is the imaginary charge that the atom would have if all of the bonds to the atom were completely ionic. By definition the oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom would have if the compound was composed of ions.
The oxidation number of an atom is zero in a neutral substance that contains atoms of only one element. Thus the atoms in O 2 O 3 P 4 S 8 and aluminum metal all have an oxidation number of 0. An oxidation number can be assigned to a given element or compound by following the following rules.
Any free element has an oxidation number equal to zero. For monoatomic ions the oxidation number always has the same value as the net charge corresponding to the ion. The hydrogen atom H exhibits an oxidation state of 1.
Assign oxidation number for CuSO_4. By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework questions. Oxidation number of C r in the following complex is.
View solution In the compounds K M n O 4 and K 2 C r 2 O 7 the highest oxidation state is of the element. Assign any lone pairs to the atom they are located on. Assign any shared pairs to the more electonegative of the two atoms sharing them winner takes all If both atoms have equal electronegativity splits the shared pair and assign one electron to each atom tie splits the prize Count all electrons assigned to an atom.