Before calculating the Cournot equilibrium point you must first know the demand curve for your market. Formula to calculate equilibrium price.
The supply curve slopes upwards since the coefficient on P in the supply curve is greater than zero and the demand.
How to calculate equilibrium price. P is the equilibrium price. Formula to calculate equilibrium price. If for instance your given the supply function and the demand function and we know that an equilibrium price is only reached when quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded we can easily solve for the equilibrium price.
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price and Quantity 1 Calculate Supply Function. In its most basic form a linear supply function looks as follows. QS mP b.
2 Calculate Demand Function. Similar to the supply function we can calculate the demand function with the help of a. When a product experiences a change in supply rather than a change in demand level the supply formula is the formula that needs to be switched to determine the products new equilibrium price.
Qs 200 150 x Price. Just like before solve. 200 150 x Price 500 - 50 x Price.
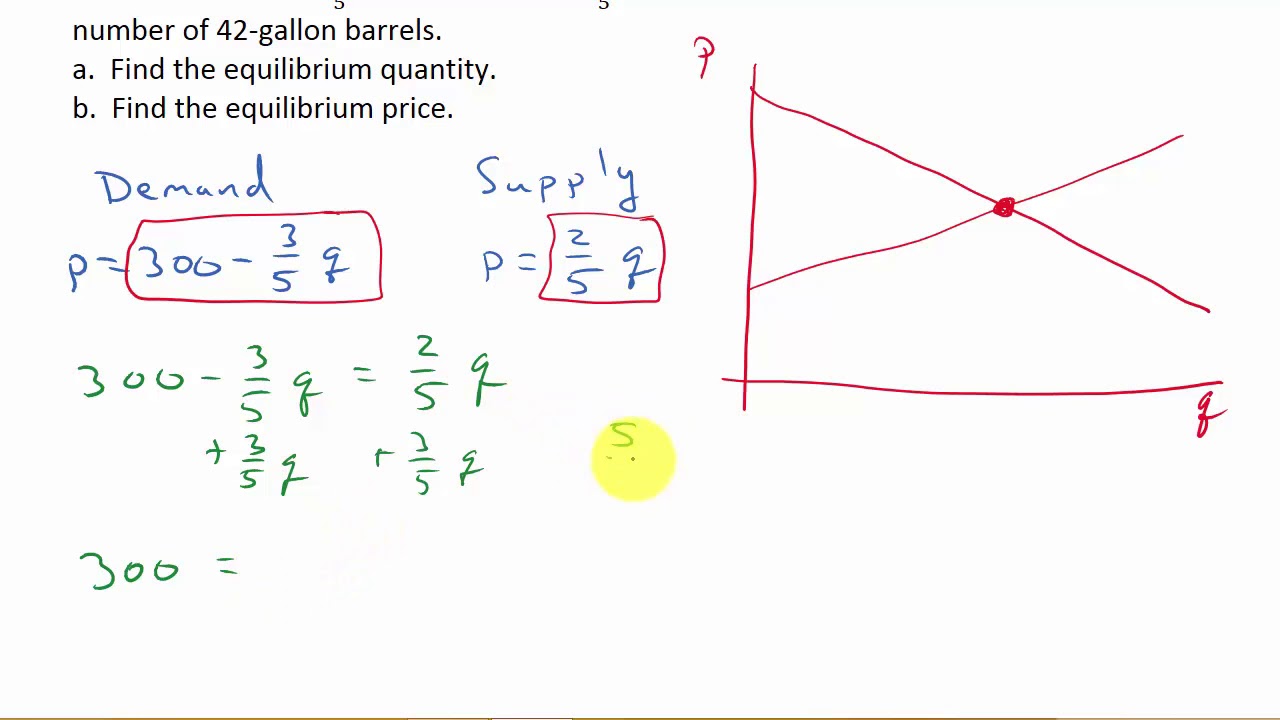
200 Price 300. To find the equilibrium price you want to find the price at which the two equations intersect. In other words find the price when the quantities Q s and Q d are the same.
This is done by simply. How does this equilibrium price and quantity calculator work. The tool was designed to help you calculate the equilibrium price and quantity for any linear quantity and supply functions both dependants on the price written as.
A bP. C dP. Where P refers to the equilibrium price.
The formula that you use to calculate equilibrium price and quantity is QdQs and then following the steps that are outlined above. How to determine the price mathematically. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied.
Add 50P to both sides of the equation. Add 100 to both sides of the equation. Divide both sides of the equation by 200.
You get P equals 200 per box. This is the equilibrium price. How to Find Equilibrium Price.
300-10p 0 10P. 300 20 20P 20 P 15. By substituting P and Q values to both demand and supply equations equilibrium price and quantity can be found as follows.
Let us suppose we have two simple supply and demand equations Qd 20 - 2P Qs -10 2P. Explanation of examples and diagrams. At this level of equilibrium the monopolist will produce OQ 1 level of output and sells it at CQ 1 price which is more than average cost DQ 1 by CD per unit.
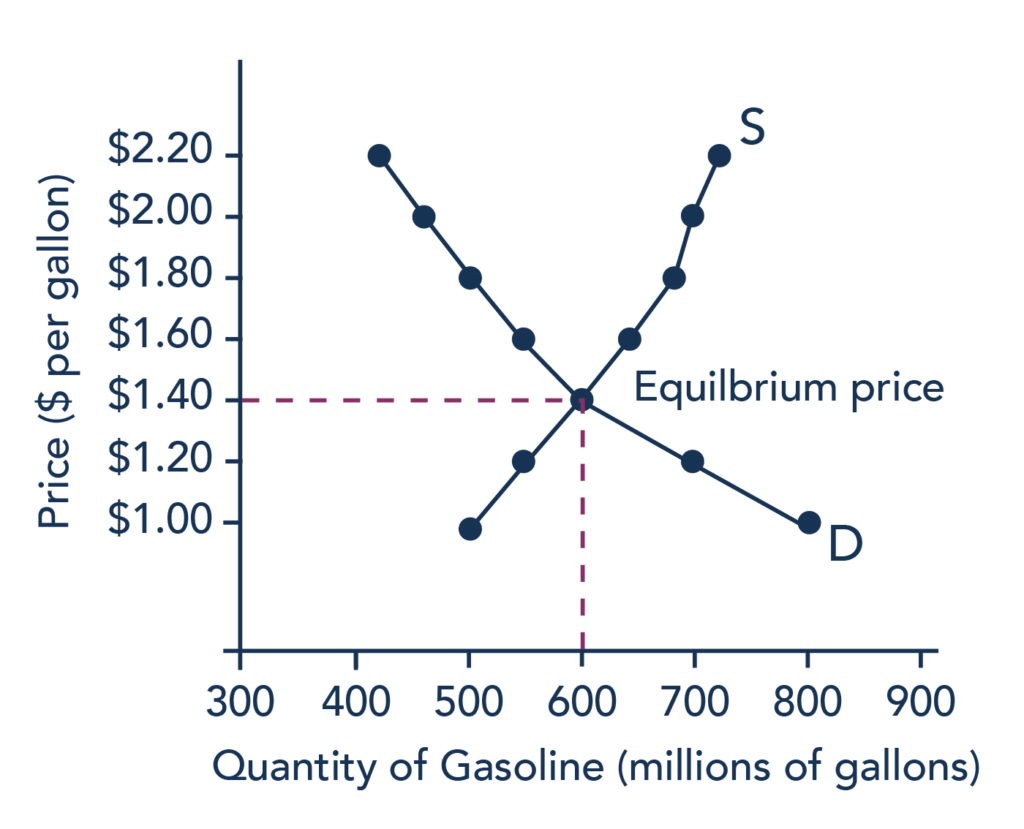
Therefore in this case total profits of the monopolist will be equal to shaded area ABDC. The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agreethat is where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy quantity demanded is equal to the amount producers want to sell quantity supplied. This mutually desired amount is called the equilibrium quantity.
To determine the equilibrium price do the following. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Add 50P to both sides of the equation.
How to Calculate an Equilibrium Equation in Economics 01. The equilibrium price and quantity in a market are located at the intersection of the market supply curve and the. The supply curve slopes upwards since the coefficient on P in the supply curve is greater than zero and the demand.
Before calculating the Cournot equilibrium point you must first know the demand curve for your market. In a demand curve the quantity demanded Q is a function of price P which is Q f P. Typically as the price goes up demand goes down but this varies with every market.
P 20 The equilibrium quantity can be determined by substituting price back into the supply or demand equation. Using the supply equation we see that the equilibrium quantity is. Q 3 20 60.
To determine the equilibrium price do the following. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Add 50P to both sides of the equation.
Equilibrium means a state of no change. Evidently at the equilibrium price both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. Technically at this price the quantity demanded by the buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by the sellers.
Both market forces of demand and supply operate in harmony at the equilibrium price.