By substituting P and Q values to both demand and supply equations equilibrium price and quantity can be found as follows. Tutorial on how to solve for quantity demanded and quantity supplied using equations algebra used in economics class.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)
When a product experiences a change in supply rather than a change in demand level the supply formula is the formula that needs to be switched to determine the products new equilibrium price.
How to determine equilibrium price. If for instance your given the supply function and the demand function and we know that an equilibrium price is only reached when quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded we can easily solve for the equilibrium price. Suppose the Supply function is Qs 40P and the demand function is Qd 1000 60P. Find the equilibrium price.
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price and Quantity 1 Calculate Supply Function. In its most basic form a linear supply function looks as follows. QS mP b.
2 Calculate Demand Function. Similar to the supply function we can calculate the demand function with the help of a. At equilibrium level of output OX price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the MR curve from below.
The firm enjoys normal profits. Now suppose demand increases from DD to D 1 D 1 and the industry is in equilibrium at point E 1 which determines the price OP 1 The new price OP 1 is less than the new market price ie OH. To find the equilibrium price you want to find the price at which the two equations intersect.
In other words find the price when the quantities Q s and Q d are the same. This is done by simply. When a product experiences a change in supply rather than a change in demand level the supply formula is the formula that needs to be switched to determine the products new equilibrium price.
Qs 200 150 x Price. Just like before solve. 200 150 x Price 500 - 50 x Price.
200 Price 300. How to determine the price mathematically. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied.
Add 50P to both sides of the equation. Add 100 to both sides of the equation. Divide both sides of the equation by 200.
You get P equals 200 per box. This is the equilibrium price. The formula that you use to calculate equilibrium price and quantity is QdQs and then following the steps that are outlined above.
How to Find Equilibrium Price. 300-10p 0 10P. 300 20 20P 20 P 15.
By substituting P and Q values to both demand and supply equations equilibrium price and quantity can be found as follows. To determine the equilibrium price do the following. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied.
Add 50P to both sides of the equation. Hence there will be one equilibrium price at which the demand by the buyers is equal to the supply by the producers. If the equilibrium is now disturbed and the price rises to OP 1 the quantity of the good supplied is OQ 2 will exceed the quantity demanded OQ 1.
Let us suppose we have two simple supply and demand equations Qd 20 - 2P Qs -10 2P. Explanation of examples and diagrams. Equilibrium Price Equilibrium means a state of no change.
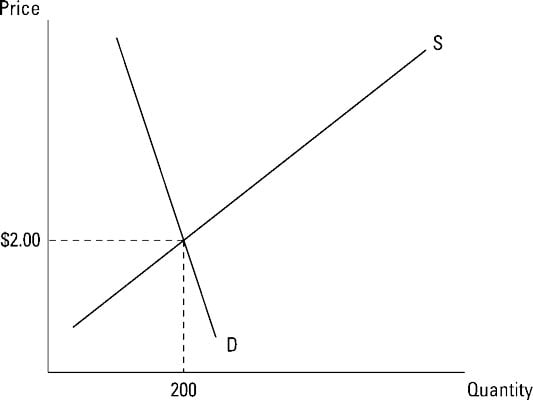
Evidently at the equilibrium price both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. Technically at this price the quantity demanded by the buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by the sellers. The equilibrium price and quantity in a market are located at the intersection of the market supply curve and the market demand curve.
While it is helpful to see this graphically its also important to be able to solve mathematically for the equilibrium price P and the equilibrium quantity Q when given specific supply and demand curves. Tutorial on how to solve for quantity demanded and quantity supplied using equations algebra used in economics class. Demonstration on how to determine equ.
In economics the equilibrium price represents the price that if practiced on the market will result in the fact that the whole quantity that is supplied is presumably sold meaning that on the market the economic forces named generally as the supply and demand are balanced and that there are no external influences that may have an impact on the price mechanism. Under monopoly for the equilibrium and price determination there are two different conditions which are. Marginal revenue must be equal to marginal cost.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity Calculator The Calculator helps calculating the Equilibrium Price and Quantity given Supply and Demand curves In microeconomics supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. The equilibrium price is established at the point where the two curves intersect. At this point the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded is equalat the equilibrium price the market is said to clear.