
The sum of the oxidation numbers in a monatomic ion is equal to the overall charge of that ion. Many atoms including most atoms with d subshells can have several different oxidation numbers.
Assigning oxidation numbers As you can see the oxidation number of Fe increases from 0 to 2 while the oxidation number of Cu 2 decreases from 2 to 0.
How to determine oxidation number. Assigning Oxidation Numbers Based on Chemical Rules 1. Determine whether the substance in question is elemental. Free uncombined elemental atoms always have an oxidation.
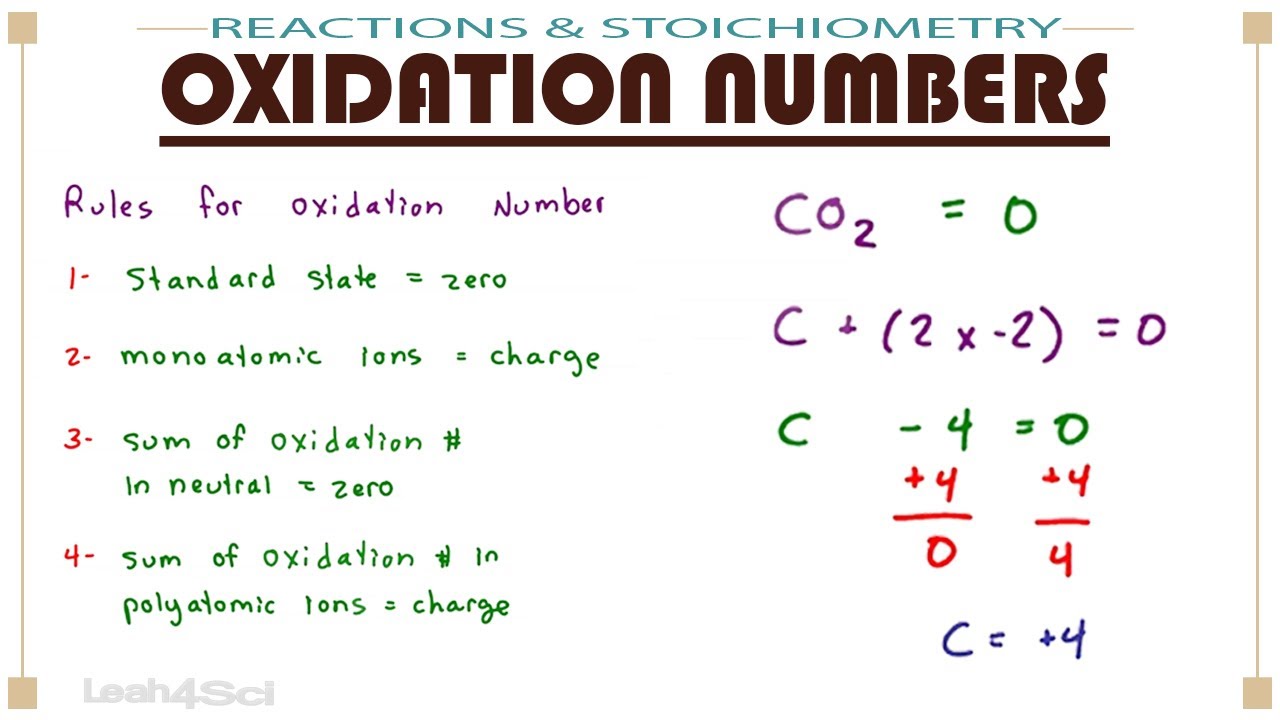
Determine whether the substance in question is an ion. Ions have oxidation numbers equal to their charge. Calculating Oxidation Numbers Any free element has an oxidation number equal to zero.
For monoatomic ions the oxidation number always has the same value as the net charge corresponding to the ion. The hydrogen atom H exhibits an oxidation state of 1. However when bonded with an element with.
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction on how to calculate oxidation numbers. It discusses how to find the oxidation states of elements. For instance if we consider the stable compound H 2 SO 4 sulfuric acid we know the net oxidation number of hydrogen and oxygen in this compound to be.
21 4-2 -6. Thus for H 2 SO 4 to be balanced sulfurs oxidation number has to be 6 which is one of its oxidation states. Incidentally it is also found in the 4 and 2 oxidation states.
However the oxidation numbers can now be determined from the number of electrons of the formally formed atomic ions. To do this one compares the number of valence electrons of the neutral atom in the PSE with the number of electrons that were mentally assigned to it using the Lewis formula. The positive oxidation state is counting the total number of electrons which have had to be removed - starting from the element.
It is also possible to remove a fifth electron to give another ion easily confused with the one before. The oxidation state of the vanadium is now 5. To find the correct oxidation number for N in NO3- the Nitrate ion and each element in the ion we use a few rules and some simple mathFirst since the N.
Notice that the zinc metal the reactant has an oxidation number of zero rule 1 and the zinc cation the product has an oxidation number of 2 rule 2. In general you can say that a substance is oxidized when theres an increase in its oxidation number. Reduction works the same way.
The newer IUPAC terminology counts the s p and d element groups one after the other so that sulphur would be in group 16. For that nomenclature you need to subtract 10 from the group number for the maximum oxidation state. Phosphorus group 15 by current terminology.
Group V by older terminology. To find the correct oxidation state of Cl in KClO3 Potassium chlorate and each element in the molecule we use a few rules and some simple mathFirst sin. The oxidation number of H is 1 H has an oxidation number of 1.
For the compound we calculate the oxidation number as follows. 2 -3 6 1 0. Therefore the oxidation number of C 2 H 6 is 0.
Many atoms including most atoms with d subshells can have several different oxidation numbers. Determining oxidation numbers from the Lewis structure Figure 1a is even easier than deducing it from the molecular formula Figure 1b. The oxidation number of each atom can be calculated by subtracting the sum of lone pairs and electrons it gains from bonds from the number of valence electrons.
To find the correct oxidation state of Sn in SnCl3 - the Trichlorostannate 1- ion and each element in the ion we use a few rules and some simple mathF. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example the oxidation number of Na is 1.
The oxidation number of N 3- is -3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is 1. The oxidation number of hydrogen is -1 in compounds containing elements that are less electronegative than hydrogen as in CaH 2.
The oxidation number of any atom in its elemental form is 0. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is 0. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a monatomic ion is equal to the overall charge of that ion.
The oxidation number of fluorine is always 1. To find the oxidation number on the periodic table the group number of the periodic table should be known. The group number indicates the number of valance shells and the atom belonging to the.
Oxidation Number Oxidation number in simple terms can be described as the number that is allocated to elements in a chemical combination. The oxidation number is basically the count of electrons that atoms in a molecule can share lose or gain while forming chemical bonds with other atoms of a different element. Assigning oxidation numbers As you can see the oxidation number of Fe increases from 0 to 2 while the oxidation number of Cu 2 decreases from 2 to 0.
Since the oxidation numbers of the chemicals in the equation changes then we can confidently say that the equation represents a redox reaction.