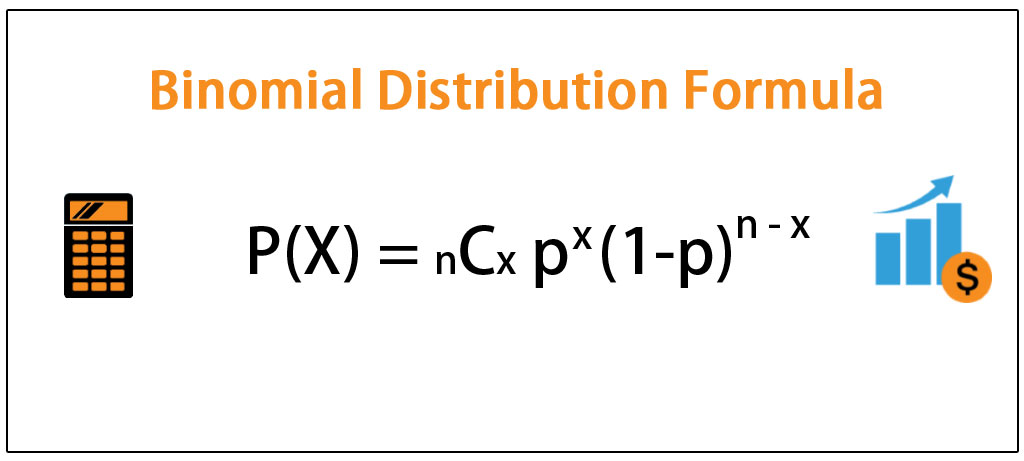
The theory of probability originated in the attempt to describe how games of chance work so it seems fitting that our discussion of the binomial distribution should involve a discussion of rolling dice and flipping coins. P X nCx px1-pn-x where p is the probability of success In the above equation n C x is used which is nothing but a combination formula.

The binomial distribution formula is.
How to do binomial probability. Please accept statistics marketing cookies to watch this video. The binomial distribution formula is. N P nCx Px 1 Pn x.
B binomial probability. X total number of successes pass or fail heads or tails etc P probability of a success on an individual trial. N number of trials.
How to Find Binomial Probabilities Using a Statistical Formula. N is the fixed number of trials. X is the specified number of successes.
N x is the number of failures. P is the probability of success on any given trial. 1 p is the probability of failure on any given trial.
Find the probability that she makes her first 2 2 free-throws and misses her third free-throw. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth if necessary. If you need to know the probability of success in k trials if n trials have been conducted and the probability of success in each trial is p this probability will be nCk p k 1-p n-k.
You will observe that this solution is of the form of a term in the binomial expansion of p and 1-p with exponent n for the kth term. The General Binomial Probability Formula. The trials are independent There are only two possible outcomes at each trial The probability of success at each trial is constant.
Have a play with the Quincunx then read Quincunx Explained to see the Binomial Distribution in action. If the probability of success on an individual trial is p then the binomial probability is n C x p x 1 p n x. Here n C x indicates the number of different combinations of x objects selected from a set of n objects.
Some textbooks use the notation n x instead of n C x. Binomial probabilities on a calculator. Some calculators offer the use of calculating binomial probabilities.
One such calculator is the Casio fx-991EX Classwiz which evaluates probability density functions and cumulative distribution functions. In the first of the two videos that follow I demonstrate how the Casio fx-991EX Classwiz calculator evaluates probability density functions and in the second how to evaluate cumulative distribution functions. Binomial Probability Calculator with a Step By Step Solution Trials n must be a whole number greater than 0.
This is the number of times the event will occur. Probability p must be a decimal between 0 and 1 and represents the probability of success on a single trial. Successes X must be a.
Formula for Binomial Distribution. Number_s required argument This is the number of successes in trials. Trials required argument This is the number of independent trials.
It must be greater than or equal to 0. Probability_s required argument This is the probability of success in each. How to show that the limit of a binomial distribution is a normal distribution.
Browse other questions tagged probability or ask your own question. Why do air entrainment admixtures improve the freeze-thaw resistance of concrete. This tutorial explains how to use the following functions on a TI-84 calculator to find binomial probabilities.
Binompdf n p x returns the probability associated with the binomial pdf. Binomcdf n p x returns the cumulative probability associated with the binomial cdf. The theory of probability originated in the attempt to describe how games of chance work so it seems fitting that our discussion of the binomial distribution should involve a discussion of rolling dice and flipping coins.
Lets imagine a simple experiment. In my hot little hand Im holding 20 identical six-sided dice. If we wanted to calculate the probability of two or more scores then we need to calculate each individual probability for the other events X23456 and add them together.
Since the probabilities for score and miss are not equal we need to calculate the probabilities the same way Sal did in this video. To compute cumulative probabilities select cumulative probability in the binomial distribution dialog. The probability of 8 or fewer successes is P X 8 0989258 or 98.
Creating a Table of Probabilities We can also use Minitab to calculate a full table of probabilities. Learn how to use the binomial probability theorem to calculate probabilities in this free math video tutorial by Marios Math Tutoring. We go through a coupl.
The probability of obtaining x successes in n independent trials of a binomial experiment is given by the following formula of binomial distribution. P X nCx px1-pn-x where p is the probability of success In the above equation n C x is used which is nothing but a combination formula. Lets now use this binomial experiment to answer a few questions.
A Find the probability that he answers 6 of the questions correctly. This is asking for the probability of 6 successes or P X 6. For finding an exact number of successes like this we should use binompdf from the calculator.