
Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. 300 20 20P 20 P 15.
π P Q q C q.
How to find the equilibrium price. P is the equilibrium price. Formula to calculate equilibrium price. If for instance your given the supply function and the demand function and we know that an equilibrium price is only reached when quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded we can easily solve for the equilibrium price.
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price and Quantity 1 Calculate Supply Function. In its most basic form a linear supply function looks as follows. QS mP b.
2 Calculate Demand Function. Similar to the supply function we can calculate the demand function with the help of a. To find the equilibrium price set these equations as equal and solve for P.
100 150 X Price 350 - 50 X Price 200 Price 250 Price 125 per box. To find the equilibrium price you want to find the price at which the two equations intersect. In other words find the price when the quantities Q s and Q d are the same.
This is done by simply. How to Find Equilibrium Price. 300-10p 0 10P.
300 20 20P 20 P 15. By substituting P and Q values to both demand and supply equations equilibrium price and quantity can be found as follows. How to determine the price mathematically.
Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Add 50P to both sides of the equation. Add 100 to both sides of the equation.
Divide both sides of the equation by 200. You get P equals 200 per box. This is the equilibrium price.
Where P refers to the equilibrium price. The algorithm behind this equilibrium price and quantity calculator consists in the following steps while it requires you to solve and know in advance both the quantity and supply functions. 1 Consider Qd quantity demanded equal to Qs quantity supplied.
How to find equilibrium price and quantity mathematically 1 Solve for the demand function and the supply function in terms of Q quantity. 2 Set Qs quantity supplied equal to Qd quantity demanded. The equations will be in terms of price P 3 Solve for P this is going to be your equilibrium.
To determine the equilibrium price do the following. Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Add 50P to both sides of the equation.
A How to find the equilibrium price The equilibrium price is found at the point from ECO 156 at Farmingdale State College. Monopolist can earn maximum profits when difference between TR and TC is maximum. By fixing different prices a monopolist tries to find out the level of output where the difference between TR and TC is maximum.
The level of output where monopolist earns maximum profits is called the equilibrium situation. Equilibrium means a state of no change. Evidently at the equilibrium price both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change.
Technically at this price the quantity demanded by the buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by the sellers. Both market forces of demand and supply operate in harmony at the equilibrium price. How to Calculate Cournot Equilibrium Once you know the optimal demand and optimal revenues for the market as a whole you can now calculate the point of equilibrium for either companys production disregarding any collusion between the two using this formula.
π P Q q C q. Let us suppose we have two simple supply and demand equations Qd 20 - 2P Qs -10 2P. Explanation of examples and diagrams.
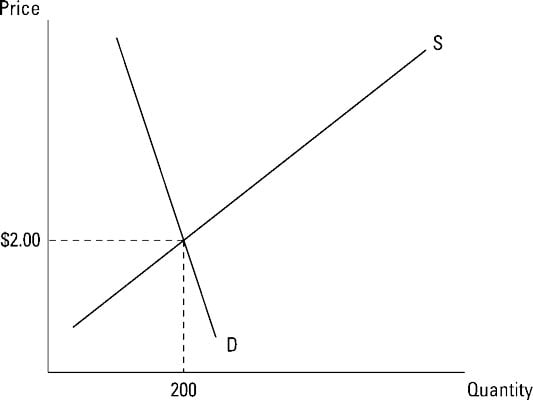
The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agreethat is where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy quantity demanded is equal to the amount producers want to sell quantity supplied. This mutually desired amount is called the equilibrium quantity. To determine the equilibrium price do the following.
Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. Add 50P to both sides of the equation. The equilibrium price and quantity in a market are located at the intersection of the market supply curve and the market demand curve.
While it is helpful to see this graphically its also important to be able to solve mathematically for the equilibrium price P and the equilibrium quantity Q when given specific supply and demand curves.