
Updated February 04 2019 Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. Energy and work have the same units.
Conservation of energy links GPE KE and work done.
Kinetic energy equation chemistry. You have a sense of what work is from regular life its things that require effort. Energy and work have the same units. Kinetic energy is the energy that comes from motion.
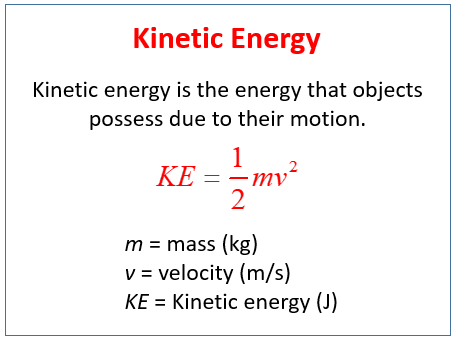
The equation for kinetic energy is. 1 K E 1 2 m v 2. Where KE is kinetic energy m is mass and v is velocity.
Calculating kinetic energy The kinetic energy of a moving object can be calculated using the equation. Kinetic energy frac 1 2 x mass x speed2 Kinetic energy frac 1 2 mv2. Kinetic energy is one type of energy store.
It is the energy stored in a moving body. The amount of kinetic energy stored in a body depends on its mass and its speed. Translational kinetic energy of a body is equal to one-half the product of its mass m and the square of its velocity v or 12mv2.
This formula is valid only for low to relatively high speeds. For extremely high-speed particles it yields values that are too small. Updated February 04 2019 Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
An object of mass m moving at velocity v has a kinetic energy equal to ½mv 2. To figure the total kinetic energy you multiply the average kinetic energy by the number of molecules you have which is nNA where n is the number of moles. NAk equals R the universal gas constant so this equation becomes the following.
In thermodynamics the change in Gibbs free energy ΔG is defined as. 62331 Δ G Δ H T Δ S. ΔG change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction.
ΔH change in enthalpy. ΔS change in entropy. Δ G o is the change in Gibbs energy when the reaction happens at Standard State 1 atm 298 K pH 7.
This equation states that the kinetic energy E k is equal to the integral of the dot product of the velocity v of a body and the infinitesimal change of the bodys momentum p. It is assumed that the body starts with no kinetic energy when it is at rest motionless. As an example to illustrate kinetic energy lets say that a 17 kg sphere is moving in a straight line with a velocity of 5 ms.
Using our equation we can determine the kinetic energy of the sphere. KE ½ 17kg 5ms² 2125 J. So the sphere has a total kinetic energy of 2125 J.
Work done is the same as energy transferred. Conservation of energy links GPE KE and work done. Power is the rate of transfer of energy or the rate of doing work.
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the average kinetic energy of a gas and the root mean square velocity as well. It contains plenty of. Solution for The average kinetic energy of the molecules in a gas sample depends only on the temperature T.
However given the same kinetic energies a lighter. Energy can be transferred between stores during motion. In the example above while the car is in motion the store that changes is the kinetic store.
To calculate kinetic energy use the equation. The formula for calculating kinetic energy KE is KE 05 x mv2. Here m stands for mass the measure of how much matter is in an object and v stands for the velocity of the object or the rate at which the object changes its position.
Rate k A The rate of a second order reaction has a rate proportional to the square of the concentration of a single reactant or else the product of the concentration of two reactants. Rate k A 2 or k A B Rate laws for individual steps must be combined to derive laws for more complex chemical reactions. The kinetic molecular theory assumes that the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of its particles as shown in the figure below.
The internal energy of an ideal gas is therefore directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. Esys 3 2 RT. Accessing the animations Order form Animations preview Free Biology animations Breathing animation Fertilisation animation Plant and animal cells The Ear animation Starch in leaf test animation Kidney animation DNA drag and drop Alveoli animation Blood clotting animation Food groups drag and drop Fossils animation Cloning animation Free Chemistry animations Periodic table Ionic bonding 1.
Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions. Kinetic Molecular Theory can be used to explain both Charles and Boyles Laws. The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to absolute temperature only.