This is called fusion. Q is the amount of energy released or absorbed during the change of phase of the substance in kJ or in BTU m is the mass of the substance in kg or in lb and.

Latent heat of fusion of water.
Latent heat of fusion equation. Specific latent heat of fusion 334 kJkg from the table above specific latent heat of fusion 334 1000 334000 Jkg. Thermal energy 05 334000 1670000 J 167 kJ Measuring. L specific latent heat of fusion of substance.
The temperature of the substance changes from t 1 low temperature to t 2 high temperature the heat which the material absorbs or releases is expressed as Q mc Δt Q mc t 2 t 1 The total amount of heat absorbed or liberated by the material is Q mL mc Δt. As there are two boundaries solidliquid and liquidgas each material has two specific latent heats. Latent heat of fusion - the amount of energy needed to melt or freeze the material at its.
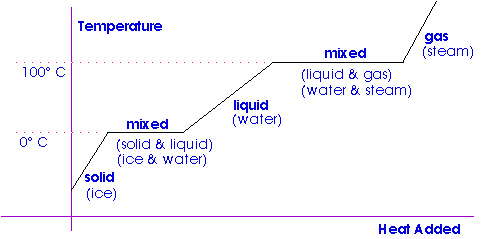
The three states of matter are solid liquid and gas. When ice a solid melts it turns into water a liquid. This is called fusion.
This equation states that the heat Q that must be added or removed for an object of mass m to change phases. We denote Individual latent heat by L. The unit of latent heat is Jkg-1 The value of latent heat is variable.
It depends on the nature of the phase change taking place. The latent heat of fusion means the change from liquid to solid. Latent Heat Formula Latent heat is energy released or absorbed by a body during a constant-temperature process for example a phase change of water from liquid to gas.
This is written as. Sensible heat mass of the body specific latent heat. Latent heat of fusion of water.
Latent heat of vaporization of water. Let us calculate latent heat by a simple expression. Determine the latent heat of a 10kg substance if the amount of heat for a phase change is 200kcal.
By using the formula Given that Mass M 10 kg Amount of heat Q 200kcal. Equation of Latent Heat of Fusion. The equation for H f is as follows.
H f ΔQ f m. Here ΔQ f is the change in the energy of the substance and m is the mass of the substance. What is Latent Heat of Vaporization.
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation relates the latent heat heat of transformation of vaporization or condensation to the rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature. Or in the case of a solid-liquid transformation it relates the latent heat of fusion or solidification to the rate of change of melting point with pressure. The formula to calculate heat of fusion is.
Q mΔH f. Note that the temperature does not actually change when matter changes state so its not in the equation or needed for the calculation. Except for melting helium heat of fusion is always a positive value.
Latent heat of fusion for water eq 335 times 105 Jkg eq. Specific heat capacity lemonade 4180 Jkg degrees C. Assume that the cup absorbs no heat during this process since its mass.
The enthalpy of fusion of a substance also known as latent heat of fusion is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy typically heat to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid at constant pressureFor example when melting 1 kg of ice at 0 C under a wide range of pressures 33355 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature. The specific latent heat of water is. L_ f3cdot34times10 5Jkg -1 for fusion solidliquid or freezing liquidsolid l_ v22cdot64times10 5Jkg -1 for.
Q m L displaystyle Q m L where. Q is the amount of energy released or absorbed during the change of phase of the substance in kJ or in BTU m is the mass of the substance in kg or in lb and. L is the specific latent heat for a particular substance kJ kg 1 or in BTU lb 1 either Lf for fusion or Lv for vaporization.
Equation refh thus gives the change in the enthalpy of the substance due to an isobaric supply of heat during vaporization. The heat of vaporization is therefore also called enthalpy of vaporization. Specific latent heat of fusion enthalpy of fusion Heat.
The latent heat we cant use the latent heat of vaporization. This is a solid turning into a liquid. Thats latent heat of fusion that we need and the latent heat of fusion for water is about 333000 joules per kilogram which gives you 999000 joules of heat in order to turn this ice at zero degree Celsius into water at zero degrees Celsius.
Thus the latent heat of fusion encompasses the process of adding heat to melt some solid. The formula for Latent heat of fusion. If m kg of the solid changes into the liquid at a constant temperature which is its melting point.
Then the heat absorbed by it means the latent heat of fusion formula will be. The Clausius-Clapeyron equation relates the latent heat heat of transformation of vaporization or condensation to the rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature. Or in the case of a solid-liquid transformation it relates the latent heat of fusion or solidification to the rate of change of melting point with pressure.