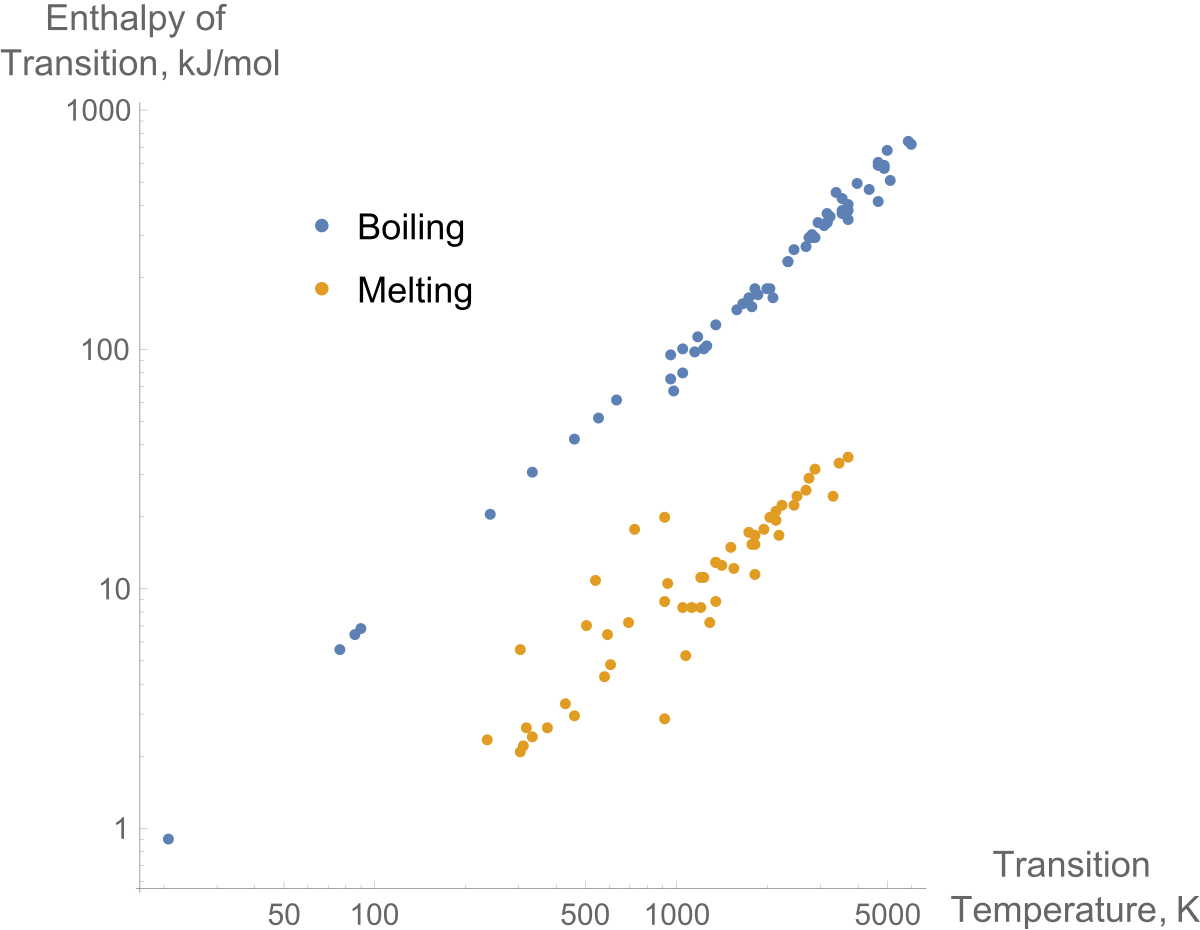
Two common forms of latent heat are latent heat of fusion melting and latent heat of vaporization boiling. For water the pressure-volume work during vaporization is to be determined in the following.
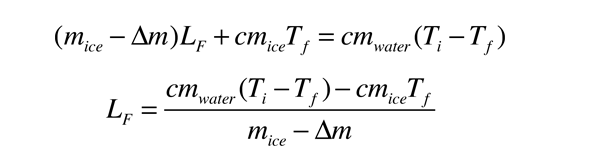
In other words if the value of the latent heat of fusion of water is 33355 kJ Kg then the value of the latent heat of solidification or freezing of water will be -33355 kJ Kg.
Latent heat of fusion of water. Specific latent heat of fusion kJkg Specific latent heat of vaporisation kJkg Water. Thus the latent heat of fusion encompasses the process of adding heat to melt some solid. The formula for Latent heat of fusion.
If m kg of the solid changes into the liquid at a constant temperature which is its melting point. Then the heat absorbed by it means the latent heat of fusion formula will be Q m times L_f. For example the latent heat of fusion of one kilogram of water which is the amount of heat energy that must be supplied to convert 1 kg of ice without changing the temperature of the environment which is kept at zero degrees celsius is 33355 kilojoules.
Similarly while ice melts it remains at 0 C 32 F and the liquid water that is formed with the latent heat of fusion is also at 0 C. The heat of fusion for water at 0 C is approximately 334 joules 797 calories per gram and the heat of vaporization at 100 C is about 2230 joules 533 calories per gram. Two common forms of latent heat are latent heat of fusion melting and latent heat of vaporization boiling.
These names describe the direction of energy flow when changing from one phase to the next. From solid to liquid and liquid to gas. In both cases the change is endothermic meaning that the system absorbs energy.
Class X Inter. Latent heat is the heat absorbed or released as the result of a phase change. This temperature change during a phase change u001bis due to the energy released from the potential energy stored in the bonds between the particles and not due to the energy release from the kinetic energy of the particle.
The heat energy input required to change water from a solid at 0 C to a liquid at 0 C is the latent heat of fusion and is 80 calories per gram of ice. Waters latent heat of fusion is the highest of all common materials. The heat required to melt a solid can be calculated as.
Q L m m 1 where. Q required heat J Btu L m latent heat of melting Jkg Btulb m mass of substance kg lb Example - Required Heat to melt Ice to Water. The heat required to melt 10 kg of ice to water can be calculated as.
Q L m m. Energy is required to change water from a solid to a liquid ie. In this experiment you will try to measure the latent heat of fusion of ice LHice the energy needed per gram to melt ice.
The needed energy will come from a cup of warm water. In other words if the value of the latent heat of fusion of water is 33355 kJ Kg then the value of the latent heat of solidification or freezing of water will be -33355 kJ Kg. Latent heat of condensation.
Latent heat of fusion of water. Latent heat of vaporization of water. Let us calculate latent heat by a simple expression.
Determine the latent heat of a 10kg substance if the amount of heat for a phase change is 200kcal. By using the formula Given that Mass M 10 kg Amount of heat Q 200kcal. The enthalpy of fusion of a substance also known as latent heat of fusion is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy typically heat to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid at constant pressureFor example when melting 1 kg of ice at 0 C under a wide range of pressures 33355 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature.
For water the pressure-volume work during vaporization is to be determined in the following. At first 1 kilogram of liquid water at a pressure of 1 bar occupies a volume of about 1 liter. After complete vaporization.
Specific latent heat of fusion enthalpy of fusion. As there can be two boundaries for change solidliquid and liquidgas each material has two specific latent heats. Latent heat of fusion - the amount of energy needed to freeze or melt the.
Water has a high latent heat of fusion so turning water into ice requires the removal of more energy than freezing liquid oxygen into solid oxygen per unit gram. Latent heat causes hurricanes to intensify. Air heats as it crosses warm water and picks up water vapor.
The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any measure of substance when it dissolves. At the point when the heat of fusion is referenced to a unit of mass it is typically called the specific heat of fusion while the molar heat of fusion alludes to the enthalpy change per measure of substance in moles. Latent Heat Flow - Latent heat is the heat when supplied to or removed from air results in a change in moisture content - the temperature of the air is not changed Liquid ammonia - Thermal Properties at saturation pressure - Density specific heat thermal conductivity viscosity and Prandtls no.
Of liquid ammonia at its saturation pressure.