9th to 12th Age. The Wooden Periodic Table Table by Theodore Gray.

The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table.
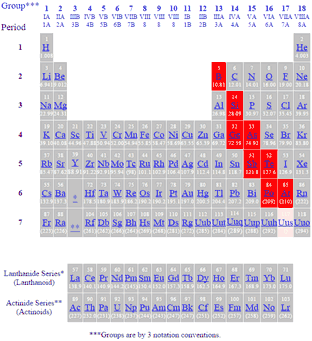
Metalloids in periodic table. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. The list of metalloids in the periodic table are as follows.
Boron B Silicon Si Germanium Ge Arsenic As Antimony Sb Tellurium Te Polonium Po. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. These elements are called metalloids.
Other authors have suggested classifying some elements as metalloids emphasizes that properties change gradually rather than abruptly as one moves across or down the periodic table. Some periodic tables distinguish elements that are metalloids and display no formal dividing line between metals and nonmetals. Metalloids are instead shown as occurring in a diagonal band or diffuse region.
The key consideration is to explain the context for the taxonomy in use. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids.
They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals.
Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals.
The term is normally applied to a group of between six and nine elements boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and possibly bismuth polonium astatine found near the center of the P-block or main block of the periodic table. There is no single property which can be used to unambiguously identify an element as a metalloid. Metalloids-Metalloids are the group of certain elements which has both the properties of the metal and the non-metal.
Metalloids are present on the non-metal side of the periodic table. Metalloids The metalloids are a group of elements in the periodic table. They are located to the right of the post-transition metals and to the left of the non-metals.
Metalloids have some properties in common with metals and some in common with non-metals. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals. The Periodic Table contains a lot of useful information on the elements.
Using it you should be able to classify all the elements in different ways. One of the best ways to classify the elements is into metals and non-metals. The Wooden Periodic Table Table by Theodore Gray.
Metalloids 7 Some books say the term Metalloid is out-dated. Nonsense its a very fine name and it accurately describes these weird in-between elements. A big hunk of Silicon is the very definition of metal-yet-not-metal.
7261 amu Number of ProtonsElectrons. 32 Number of Neutrons. 41 Date of Discovery.
The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table. Because these elements have intermediate properties its sort of a judgment call as to whether a particular element is a metalloid or should be assigned to one of the other groups. 70 metals or metalloids are found between nonmetals on the periodic table of the elements.
Elements in this range have properties intermediate between nonmetals and metals. The exact elements considered to be metalloids are somewhat up for debate with different classification systems considering different elements metalloids. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND.
Metals Nonmetals Metalloids periodic table ID. 9th to 12th Age. Periodic Table Other contents.
Add to my workbooks 5 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams.