
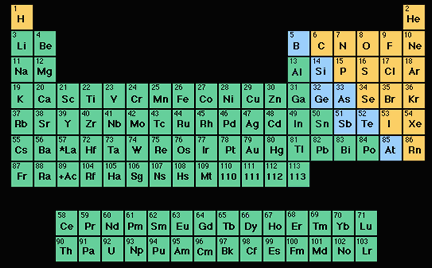
Metals are at the left nonmetals are at the right and metalloids straddle a zig-zag line that separates metals from nonmetals. Typical nonmetals have a dull coloured or colourless appearance.
Taking physical properties into consideration they are more like the nonmetals but under certain circumstances contrary to the expected behaviour many of them can be made to conduct electricity.
Metals non metals metalloids. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. These elements are called metalloids. The metalloids or semimetals have properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals.
Metalloids tend to be economically important because of their unique conductivity properties they only partially conduct electricity which make them valuable in the semiconductor and computer chip industry. Metalloids are metallic-looking brittle solids that are either semiconductors or exist in semiconducting forms and have amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides. Typical nonmetals have a dull coloured or colourless appearance.
Are brittle when solid. Are poor conductors of heat and electricity. And have acidic oxides.
The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
To understand the basic properties separating Metals from Nonmentals and Metalloids An element is the simplest form of matter that cannot be split into simpler substances or built from simpler substances by any ordinary chemical or physical method. Metals nonmetals and metalloids are elements that are found in the earth. Most of these elements are used in various applications.
The main difference between metals nonmetals and metalloids is that metals show the highest degree of metallic behavior and nonmetals do not show metallic behavior whereas metalloids show some degree of metallic behavior. A non metal is a material which do not have properties of metals like lustre. They are non malleable non ductile non sonorous and bad conductor of heat and electricity.
Example- Carbon Sulphur Phosphorous. A metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Metalloids are located to the right of metals and to the left of nonmetals in the periodic table.
They are solids under standard conditions and can easily form alloys with Metals. The alkali metals lithium sodium potassium rubidium cesium and francium constitute group 1 of the periodic table. Although hydrogen is in group 1 and also in group 17 it is a nonmetal and deserves separate consideration later in this tutorial.
Examples of metals are Lithium Sodium Calcium Magnesium Barium Lead and Indium. Examples of non-metals are Iodine Bromine Helium Neon and Argon while that of metalloids are Arsenic Tellurium Antimony Polonium Tennessine etc. Similarities between Metals Non-Metals and Metalloids.
Both loss or gain electrons in chemical reactions. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND. Introduction to Metals Non Metals and Metalloids.
Discussion of the properties of each. Metals are the elements which exhibit the highest degree of metallic behavior is known as metals on the contrary Non-metals are such elements which do not possess any metallic behavior and Metalloids are those elements that possess some of the properties like metal while some like non-metal. Most elements are metals.
This includes the alkali metals alkaline earth metals transition metals lanthanides and actinides. On the periodic table metals are separated from nonmetals by a zig-zag line stepping through carbon phosphorus selenium iodine and radon. These elements and those to the right of them are nonmetals.
The seven metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and polonium. The three types of elements occupy their own places in the Periodic Table. Metals are at the left nonmetals are at the right and metalloids straddle a zig-zag line that separates metals from nonmetals.
METALLOIDS SEMI METALS It is very much clear from the periodic table that non-metallic character increases as we move from left to right across a row. It has been found that some elements lying at the border of metallic and non-metallic behaviour possess the properties that are characteristic of both metals and non-metals. The metalloids are intermediate in their properties between metals and nonmetals.
Taking physical properties into consideration they are more like the nonmetals but under certain circumstances contrary to the expected behaviour many of them can be made to conduct electricity.