Similarly if the object is at rest it will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Newtons Second Law of Motion defines the relationship between acceleration force and mass.

Isaac Newton laid down 3 laws of motion more than three hundred y.
Newtons laws of motion. In classical mechanics Newtons laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. The first law states that an object either remains at rest or continues to move at a constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an external force. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the force applied or for an object with constant mass that the net force on an object is equa.
Newtons laws of motion relate an objects motion to the forces acting on it. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. In the second law the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration.
In the third law when two objects interact they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction. According to Newtons first law of motion an object remains in the same state of motion unless a resultant force acts on it. If the resultant force on an object is zero this means.
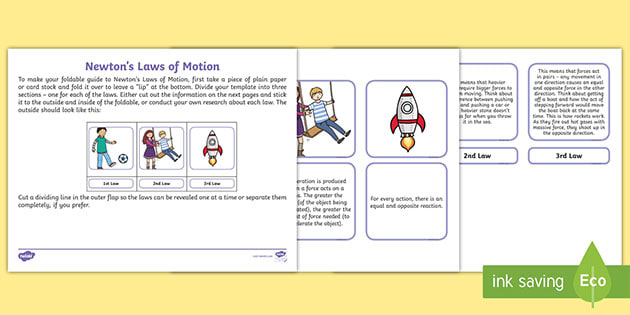
Newtons first law states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia. Newtons First Law of Motion.
Newtons First Law of Motion states that an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless an external force acts upon it. Similarly if the object is at rest it will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Newtons First Law of Motion is also known as the Law of Inertia.
Newtons First Law of Motion states that in order for the motion of an object to change a force must act upon it. This is a concept generally called inertia. Newtons Second Law of Motion defines the relationship between acceleration force and mass.
Newtons First Law of Motion Every body continues in a state of rest or if uniform motion in a straight line unless it is acted upon by an external force and is compelled to change its state. This law gives us a definition of force. Force is an agent which produces acceleration.
Newtons laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it and its motion in response to those forces. Newtons First Law of Motion states that objects with balanced forces acting on them will stay at rest or stay in constant motion. Newton discovered that objects will continue to do what they are.
Newtons first law of motion A body continues in a state of rest or uniform velocity unless acted upon by an external force This is also known as the law of inertia and means that something will either stay still or stay moving unless a force acts on it. Newtons laws refer to the motion of objects in an inertial reference frame which can be described as a system in which an object remains at rest or moves with constant linear velocity unless acted upon by external forces. Newton found that movement within such a system could be expressed using three simple laws.
Newtons Three Laws of Motion. Newton proposed three laws of motion that explain interactions between solid objects describing force inertia and reaction forces. Newtons three laws of motion were the first quantitative and predictive laws of mechanics.
Sir Isaac Newton first presented his three laws of motion in the Principia Mathematica Philosophiae Naturalis in 1686. His first law states that every object remains at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia.
Motion and forces are everywhere. Why do things move. Why do they stop.
How do forces work. Isaac Newton laid down 3 laws of motion more than three hundred y. What are some daily life examples of Newtons 1st 2nd and 3rd laws of motion.
The motion of a ball falling through the atmosphere or a model rocket being launched up into the atmosphere are both. You hit a wall with a certain amount of force and the wall returns that same amount of force. SUBSCRIBE FOR MORE VIDEOS.
Httpbitly2F48qzK FREE DOWNLOAD 7 SECRETS OF MAKING YOUR OWN SONGS. Newtons Third Law to describe the motion of an untied balloon. You may have heard Newtons Third Law as.
For every action is an equal and opposite reaction. However try and avoid using this definition since it is unclear on what the forces are acting on and can be misleading. Sir Isaac Newtons three laws of motion describe the motion of massive bodies and how they interact.
While Newtons laws may seem obvious to us today more than three centuries ago they were. A scientist named Isaac Newton came up with three Laws of Motion to describe how things move scientifically. He also described how gravity works which is an important force that affects everything.
First Law of Motion The first law says that any object in motion will continue to move in the same direction and speed unless forces act on it.