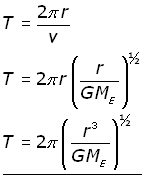
This means the track of the satellite as seen from the central body will repeat exactly after a fixed number of orbits. Orbital period P2pilargefrac637814hvhspace10px smallsec.
A geosynchronous orbit sometimes abbreviated GSO is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earths rotation on its axis 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds one sidereal dayThe synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that for an observer on Earths surface an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period.
Period of satellite orbit. The period of a satellite is the time it takes it to make one full orbit around an object. The period of the Earth as it travels around the sun is one year. If you know the satellites speed and the radius at which it orbits you can figure out its period.
You can calculate the speed of a satellite around an object using the equation. Geostationary satellites Geostationary satellites take 24 hours to orbit the Earth. This is the same time that Earth takes to complete one rotation and so the satellite always remains above the.
The orbital period is the time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object and applies in astronomy usually to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun moons orbiting planets exoplanets orbiting other stars or binary stars. For objects in the Solar System this is often referred to as the sidereal period determined by a 360 revolution of one celestial. Shows how to calculate the orbital period of a Satellite.
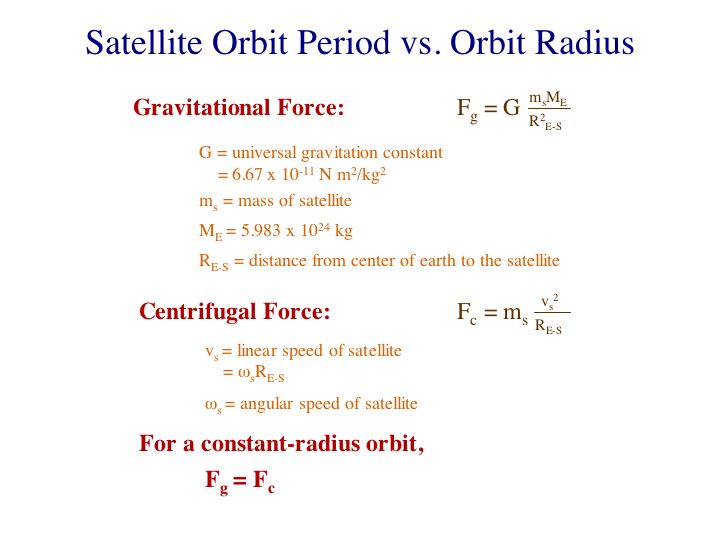
The equation for orbital period is derived from Newtons second law and Newtons Law of universal. An orbital period is defined as the total time it takes a satellite or orbiting object to make one complete rotation around another larger object. A satellite in a Molniya orbit takes 12 hours to complete its orbit but it spends about two-thirds of that time over one hemisphere.
Like a semi-synchronous orbit a satellite in the Molniya orbit passes over the same path every 24 hours. This type of orbit is useful for communications in the far north or south. An orbit whose period is a rational multiple of the average rotational period of the body being orbited and in the same direction of rotation as that body.
This means the track of the satellite as seen from the central body will repeat exactly after a fixed number of orbits. In practice only 11 ratio geosynchronous and 12 ratios semi-synchronous are common. An orbit where the satellite has an orbital period equal to the average rotational period earths is.
23 hours 56 minutes 4091 seconds of the body being orbited and in the same direction of rotation as. Hhmmss normalsize flight velocity vsqrtlargefrac3986005637814hhspace10px smallkms. Orbital period P2pilargefrac637814hvhspace10px smallsec.
Find the orbital period of a satellite in a circular orbit 36000 km above the earths surface if the earths radius is 6400 km. The outline of a communications satellite antenna pattern on the earth is known as. Calculate the length of the path to a geostationary satellite from.
A geosynchronous satellite is a satellite that orbits the earth with an orbital period of 24 hours thus matching the period of the earths rotational motion. A special class of geosynchronous satellites is a geostationary satellite. The International Space Station orbits Earth once about every 92 minutes flying at about 250 miles 400 km above sea level.
Two bodies of different masses orbiting a common barycenter. The relative sizes and type of orbit are similar to the Pluto Charon system. A low Earth orbit LEO is an Earth-centred orbit with an altitude of 2000 km 1200 mi or less approximately one-third of the radius of Earth or with at least 1125 periods per day an orbital period of 128 minutes or less and an eccentricity less than 025.
Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO. There is a large variety of other sources that define LEO in terms of. The satellite orbit period formula can be expressed as.
T 4π2r3GM Satellite Mean Orbital Radius r 3 T2GM4π2. The time period of a satellite is the time taken by it to go once around the earth. Therefore Putting g 98 ms-2 and R 64 x 106 m in iv we get T 846 minutes that is the time period of a satellite revolving near the surface of the earth.
The orbital period of a geosynchronous satellite is a sidereal day ie 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds which is why it seems to stay in place over a single longitude although it may drift southnorth depending upon the orbits inclination with Earths equatorial plane. Geosynchronous vs Geostationary Satellites. A geosynchronous orbit sometimes abbreviated GSO is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earths rotation on its axis 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds one sidereal dayThe synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that for an observer on Earths surface an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period.
Period of the satellite is 24 hr. Such a satellite is called geosynchronous satellite and is used for communication broadcasting and weather forecasting. Such a satellite moves in the same direction as that of the rotation of the earth and its orbit is in the equatorial plane.