
Elements that are in the same period have chemical properties that are not all that similar. When going across Period 2 and Period 3 from left to right.
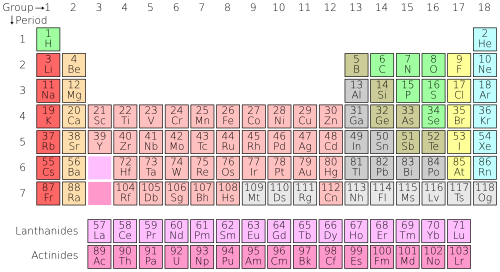
Each horizontal row of elements in the Periodic Table is known as a period.
Periods on a periodic table. Period 2 Lithium Li is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. In its non-ionized state it is one of the most. Beryllium Be has one of the highest melting points of all the light metals.
Small amounts of beryllium were. Boron B does not occur naturally as a free element but. Here are the main features of the table.
The horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same group are similar to each other the metals are on the left and the non-metals are on the right hydrogen is a non-metal but is often put in the middle the main. A period is a horizontal row of the periodic table. There are seven periods in the periodic table with each one beginning at the far left.
A new period begins when a new principal energy level begins filling with electrons. Period 1 has only two elements hydrogen and helium while periods 2 and 3 have 8 elements. The periodic table codifies the energy levels in periods the rows on the table.
The simplest atoms hydrogen and helium are found in row 1 or the first period. These atoms have electrons occupying the energy level n1. Moving down row 2 or period 2 contains the elements Li lithium through Ne neon.
The periodic table also known as the periodic table of elements is a tabular display of the chemical elements which are arranged by atomic number electron configuration and recurring chemical propertiesThe structure of the table shows periodic trendsThe seven rows of the table called periods generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. Each horizontal row of elements in the Periodic Table is known as a period. The Periodic Table consists of seven periods from Period 1 to Period 7.
Table shows the changes in the proton numbers and number of valence electrons when going across Period 2. When going across Period 2 and Period 3 from left to right. A period may be defined as horizontal row in the periodic table.
In terms of electronic structure of the atom a period constitutes a series of elements whose atoms have the same number of electron shells ie. Principal quantum number n. Periods in the periodic table.
In each period horizontal row the atomic numbers increase from left to right. The periods are numbered 1 through 7 on the left-hand side of the table. Elements that are in the same period have chemical properties that are not all that similar.
The modern periodic table is based closely on the ideas he used. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are. This Groups and Periods on the Periodic Table Worksheet is a great way to stimulate confidence and comprehension of the periodic table.
Students are asked to answer a series of questions related to the periodic table along with labelling group and period numbers. Designed for KS3 Chemistry students this resource can also be used in KS4 classes. The periods on the Periodic table represents the number of shells or orbits of an atom.
The rows of the periodic table are called periods. An elements period number is the highest unexcited energy level for an electron of that element. Columns of elements help to distinguish groups in the periodic table.
Elements within a group share several common properties and often have the same outer electron arrangement. Periods of the Periodic Table If you can locate an element on the Periodic Table you can use the elements position to figure out the energy level of the elements valence electrons. A period is a horizontal row of elements on the periodic table.
For example the elements sodium Na and magnesium Mg are both in period 3. View periodic table basicspdf from CHEM NA at Union County Vocational Technical School. Name_ Date_ Period_ Chem I Periodic Table WS 2 Periodic Table Basics 1.
Why do the elements chlorine and. Interactive periodic table showing names electrons and oxidation states. Visualize trends 3D orbitals isotopes and mix compounds.
Each period starts with group IA 1 and ends in group VIIIA 0 or 18 1. Periodic trends arise from the changes in the atomic structure of the chemical elements within their respective periods horizontal rows and groups in the periodic table. These laws enable the chemical elements to be organized in the periodic table based on their atomic structures and properties.
Due to the periodic trends the unknown. Synthesizing new superheavy elements to open up the eighth period of the periodic table. Superheavy chemistry one atom at a time.