The distribution of sugar in childrens cereals is skewed to the left. A few items fail immediately and many more items.
A left skewed distribution has a long left tail.
Skewed left box plot. The box plot will look as if the box was shifted to the left so that the right tail will be longer and the median will be closer to the left line of the box in the box plot. If the distribution is skewed to the left most values are large but there are a few exceptionally small ones. When the median is closer to the top of the box and the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box the distribution is left skewed.
When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side the distribution is symmetrical. Examples of Skewed Distributions. A left-skewed distribution along with its corresponding box plot.
Left-skewed boxplot with distribution curve. Q1 Q2 Q3. The box-and-whisker plot also known simply as the box plot is useful in visualizing skewness or lack thereof in data.
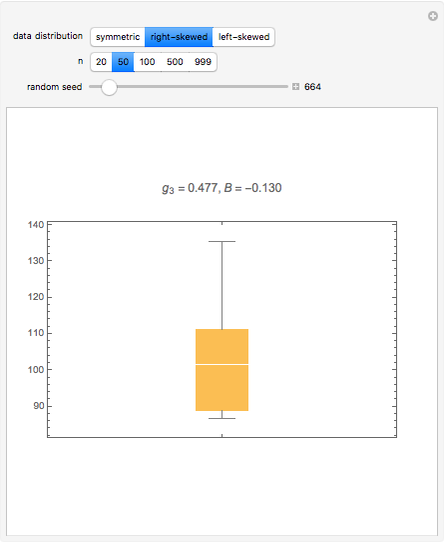
The usual form of the box plot shown in the graphic shows the 25 and 75 quartiles and at the bottom and top of the box respectively. The median is shown by the horizontal line drawn through the box. A distribution that is skewed left has exactly the opposite characteristics of one that is skewed right.
The mean is typically less than the median. The tail of the distribution is longer on the left hand side than on the right hand side. The median is closer to the third quartile than to the first quartile.
When the median is closer to the top of the box and if the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box then the distribution is negatively skewed skewed left. Box plots are useful as they show the dispersion of a data set. For a distribution that is positively skewed the box plot will show the median closer to the lower or bottom quartile.
A distribution is considered Positively Skewed when mean median. It means the data constitute higher frequency of high valued scores. A right skewed distribution has a long right tail.
Thats because there is a long tail in the negative direction on the number line. People sometimes say it is skewed to the left the long tail is on the left hand side the mean is also on the left of the peak. A left skewed distribution has a long left tail.
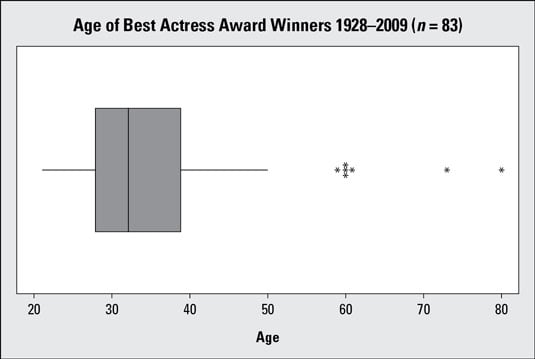
While its a pretty crude instrument which is why I looked at the QQ-plot there are several indications of skewness in a boxplot - if theres at least one point marked as an outlier theres potentially at least three. In this sample n100 the outer points green mark the extremes and with the median suggest left skewness. In descriptive statistics a box plot or boxplot is a method for graphically depicting groups of numerical data through their quartilesBox plots may also have lines extending from the boxes whiskers indicating variability outside the upper and lower quartiles hence the terms box-and-whisker plot and box-and-whisker diagramOutliers may be plotted as individual points.
A box and whisker plot can show whether a data set is symmetrical positively skewed or negatively skewed. This box and whisker plot is not symmetrical because the whiskers are not the same length and the median is not in the centre of the box. The whisker on the left is a bit longer than the whisker on the right which shows that the data on the left of the box is more spread out.
Skewness indicates that the data may not be normally distributed. The following boxplots are skewed. The boxplot with right-skewed data shows wait times.
Most of the wait times are relatively short and only a few wait times are long. The boxplot with left-skewed data shows failure time data. A few items fail immediately and many more items.
This can help aid the at-a-glance aspect of the box plot to tell if data is symmetric or skewed. When one of these alternative whisker specifications is used it is a good idea to note this on or near the plot to avoid confusion with the traditional whisker length formula. Note that this asymmetry in the box of a boxplot is related to a measure of skewness called the quartile skewness Also see here In small samples from symmetric distributions the median may frequently be much closer to one hinge effectively quartile than the other.
A cluster of data on the right with a tail of data tapering off to the left. A left skewed distribution has a lot of data at higher variable values with smaller amounts of data at lower variable values. The distribution of sugar in childrens cereals is skewed to the left.
When a box plot is left-skewed values gather at the upper end making a short and tight section there. To the left of that crowd data points spread out creating a longer tail. Box plots are like the base of distribution curves.
Skewness suggests that data may not be normally distributed. The distribution is negatively skewed skewed left when the median is closer to the top of the box and if the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box. Hence Box plot is also useful to.
A box plot also known as box and whisker plot is a type of chart often used in descriptive data analysis to visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles or percentiles averages.