
The framework for the idea of endosymbiosis began with work done by Andreas Schimper in 1883. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell.
The Theory of Endosymbiosis.
The theory of endosymbiosis. Updated January 09 2020 The endosymbiotic theory is the accepted mechanism for how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells. It involves a cooperative relationship between two cells which allow both to surviveand eventually led to the development of all life on Earth. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in todays eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
In this theory the first eukaryotic cell was probably an amoeba-like cell that got nutrients by phagocytosis and contained a nucleus that formed when a piece of the cytoplasmic membrane pinched off around the chromosomes. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in prokaryotic cells were once from eukaryotic organisms. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells.
The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion. The Theory of Endosymbiosis. Post author By a b.
Post date February 15 2021. The mitochondria and chloroplast are thought to have once been free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by an early eukaryote and incorporated into the functioning of that cell. For this discussion describe the theory of endosymbiosis in your own words and identify.
Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates to t.
Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well.
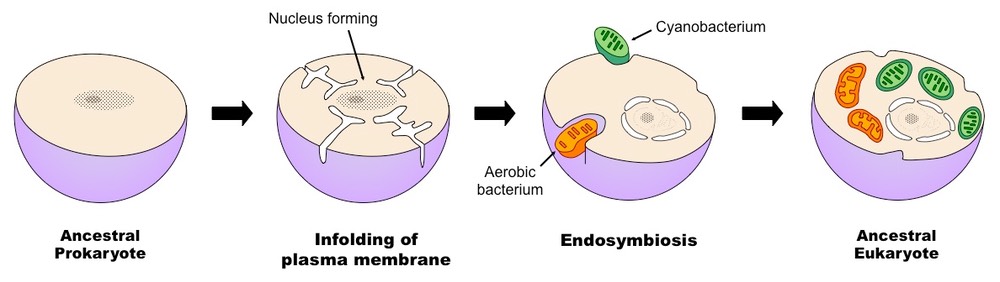
An endosymbiont is a cell which lives inside another cell with mutual benefit Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis The engulfed prokaryotic cell remained undigested as it contributed new functionality to the engulfing cell eg. The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondriaof eukaryotesevolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell. The chloroplastsof red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacteriumliving within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell.
A representation of the endosymbiotic theory An endosymbiont or endobiont is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often though not always in a mutualistic relationship. The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek.
In her theory of endosymbiosis Lynn Margulis emphasizes that during the history of life symbiosis has played a role not just once or twice but over and over again. Instead of the traditional tree of life branching out from a few common ancestors to many descendent species Margulis proposes that branches have separated and then come. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory.
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells.
Endosymbiosis–the symbiotic relationship where one symbiotic organism living inside another. Where did this theory come from. Biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the idea of endosymbiosis about 50 years ago.
She proposed it as the explanation for how complex cells evolved. The hypothesized process by which prokaryotes gave rise to the first eukaryotic cells is known as endosymbiosis and certainly ranks among the most important evolutionary events. The framework for the idea of endosymbiosis began with work done by Andreas Schimper in 1883.
Schimper a botanist born in France in 1856 made the observation that the chloroplasts that are found in photosynthetic organisms had many similar characteristics to cyanobacteria. Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. The Theory of Endosymbiosis.
The mitochondria and chloroplast are thought to have once been free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by an early eukaryote and incorporated into the functioning of that cell. For this discussion describe the theory of endosymbiosis in your own words and identify and discuss one line the evidence for this.