Whenever you report a confidence interval you must state the confidence level like this. Most studies report the 95 confidence interval 95CI.
A 99 confidence interval is wider than a 95 confidence interval.
Understanding confidence intervals for dummies. Dence level of the CI. You can calculate a CI for any confidence level you like but the most commonly used value is 95 percent. Whenever you report a confidence interval you must state the confidence level like this.
95 CI 114126. This short video gives an explanation of the concept of confidence intervals with helpful diagrams and examples. A good follow-up to check understanding is.
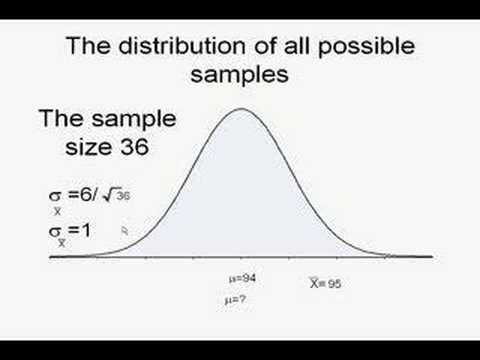
Dont know what to make of a 95 confidence interval when reading a scientific article. We will explain what it is how its calculated and how to interpret i. The confidence interval is based on the observations from a sample and hence differs from sample to sample.
The likelihood that the parameter will be in the interval is called the confidence level and the end points of the confidence interval are referred to as confidence limits. Confidence intervals are frequently reported in scientific literature and indicate how close research results are to reality or how reliable they are based on statistical theory. The confidence interval uses the sample to estimate the interval of probable values of the population.
The parameters of the population. Confidence interval is a concept born of frequentist statistics whereas the statement expresses a Bayesian belief. In this article we will find out through simulated experiments on real data what confidence interval really means.
The difference between frequentist and Bayesian statistic s is fundamental. Although these aspects are different all of these confidence intervals are united by the same overall format. Some common confidence intervals are those for a population mean population variance population proportion the difference of two population means and the difference of two population proportions.
95 confidence interval 079 to 115 is an interval estimate for the population parameter of the relative risk of postpartum haemorrhage representing the inaccuracy of the sample in estimating. A confidence interval in statistics refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. Confidence intervals measure the.
It explains that confidence intervals are used because a study recruits only a small sample of the overall population so by having an upper and lower confidence limit we can infer that the true population effect lies between these two points. Most studies report the 95 confidence interval 95CI. Degree of confidence and is called a confidence interval1 For example with 95 CIs we can be 95 certain that the intervals cover the true population value.
T1 - A practical guide for understanding confidence intervals and P values. AU - Wang Eric W. AU - Ghogomu Nsangou.
A 99 confidence interval is wider than a 95 confidence interval. This is the confidence interval. Usually the confidence interval is set at 95 which tells you that if you did this study 100 times 95 out of 100 times the true measure would lie between the two confidence intervals.
Lets look at another interesting study. The 95 confidence interval is presented as standard in research. Confidence intervals with different percentages can be usedfor example 90 and 99.
A 99 confidence interval for the population relative risk in postpartum haemorrhage would be wider than the 95 confidence interval presented c is false. This is because a 99 confidence. In statistics a confidence interval is an educated guess about some characteristic of the population.
A confidence interval contains an initial estimate plus or minus a margin of error the amount by which you expect your results to vary if a different sample were taken. Or Confidence Intervals for Dummies Joseph Lockhart Department of State Hospitals California Direct correspondence to. Lockhart PhD A BPP 1305 North.
The confidence interval represents the frequency ie. Proportion of possible confidence intervals that contain the true value of the unknown population parameter. So if we take infinitely many samples and find the confidence interval range for each of these samples then the number of intervals that contain the population parameter is equal to.
A sister version of the confidence curve ccσ is the cumulative distribution function Cσ shown in Figure B. Its often called the CD the confidence distribution. It starts at level 0 far to the left and climbs up to level 1 far to the right.
It passes the magical midpoint 050 at the median confidence point estimate 3226. The newly released sixth edition of the APA Publication Manual states that estimates of appropriate effect sizes and confidence intervals are the minimum expectations APA 2009 p. An increasing number of journals echo this sentiment.
For example an editorial in Neuropsychology stated that effect sizes should always be reported along with confidence intervals.