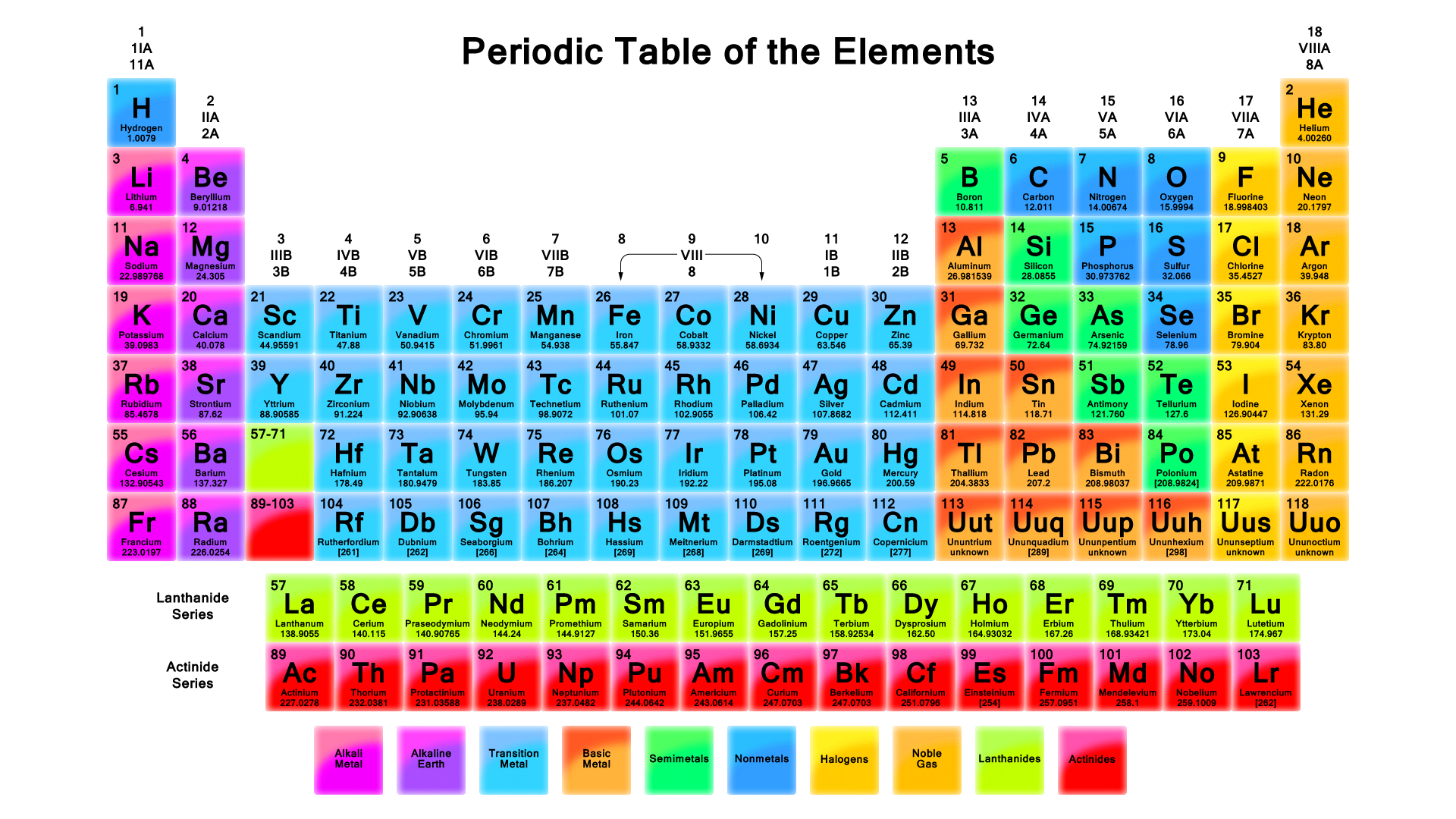
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The staircase-shaped line is a typical example of the arbitrary metalnonmetal dividing line found on some periodic tables.
They are found in a stair step line that helps differentiate metals from non-metals in this element table.
What are the metalloids in the periodic table. The metalloids also known as semi-metals are placed between metals and non-metals in the periodic table of elements. There are seven elements that are classified as metalloids and placed in Group 13 14 15 16 and 17. They are found in a stair step line that helps differentiate metals from non-metals in this element table.
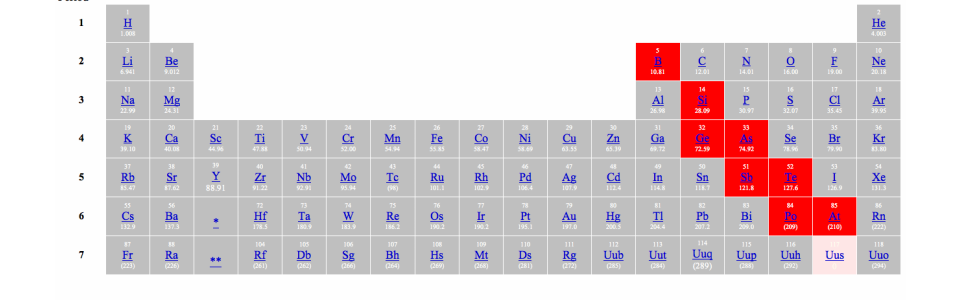
Recognition status as metalloids of some elements in the p-block of the periodic table. Percentages are median appearance frequencies in the lists of metalloids. The staircase-shaped line is a typical example of the arbitrary metalnonmetal dividing line found on some periodic tables.
The elements on the periodic table can be grouped as metals nonmetals or metalloids. All of the metalloids have some properties of both metals and nonmetals and are located directly in between. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table.
Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. One or more of carbon aluminium phosphorus selenium tin or bismuth these being periodic table neighbours of the elements commonly classified as metalloids are sometimes recognised as metalloids. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals.
The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image.
The elements which are found in the step-like line between metals and nonmetals of the periodic table are known as the metalloids. Antimony Sb germanium Ge silicon Si arsenic As tellurium Te polonium Po boron B and astatine At. What is the definition of the term metalloid.
The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84.
Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals. A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the left-hand side of the period. Metalloids are chemical elements that display properties of both metals and nonmetals.
On the periodic table metalloids are found along a zig-zag line between boron and aluminum down to polonium and astatine. Usually the semimetals or metalloids are listed as boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and polonium. The six commonly recognised metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony and tellurium.
Five elements are less frequently so classified. Carbon aluminium selenium polonium and astatine. Metalloids are elements found between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table of the elements.
They are also called semimetals. Metalloids have properties that are between the properties of nonmetals and metals. The Metalloids is the term given to the elements in the periodic table that exist between metals and non metals on the right hand side.
These are elements that exhibit both properties of metals and non metals. Metalloids are a group of elements that run from Boron to Polonium in the periodic table that bridge the metals and non metals. Metalloids usually form amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides.
Most of the other physical and chemical properties of metalloids are intermediate in nature. The 7 elements classified as metalloids are located in Groups 13 14 15 16 and 17 elements of the periodic table. Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
These elements are called metalloids or. The Periodic Table Is Made Up Of Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids. Metals exhibit the following properties.
What are metalloids on the periodic table. All of the metalloids have some properties of both metals and nonmetals and are located directly in between the two groups on the periodic table. Usually solid at room temperature mercury is an.