
Silicon has a metallic lustre but it is a poor conductor and. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals.
Silicon has a metallic lustre but it is a poor conductor and.
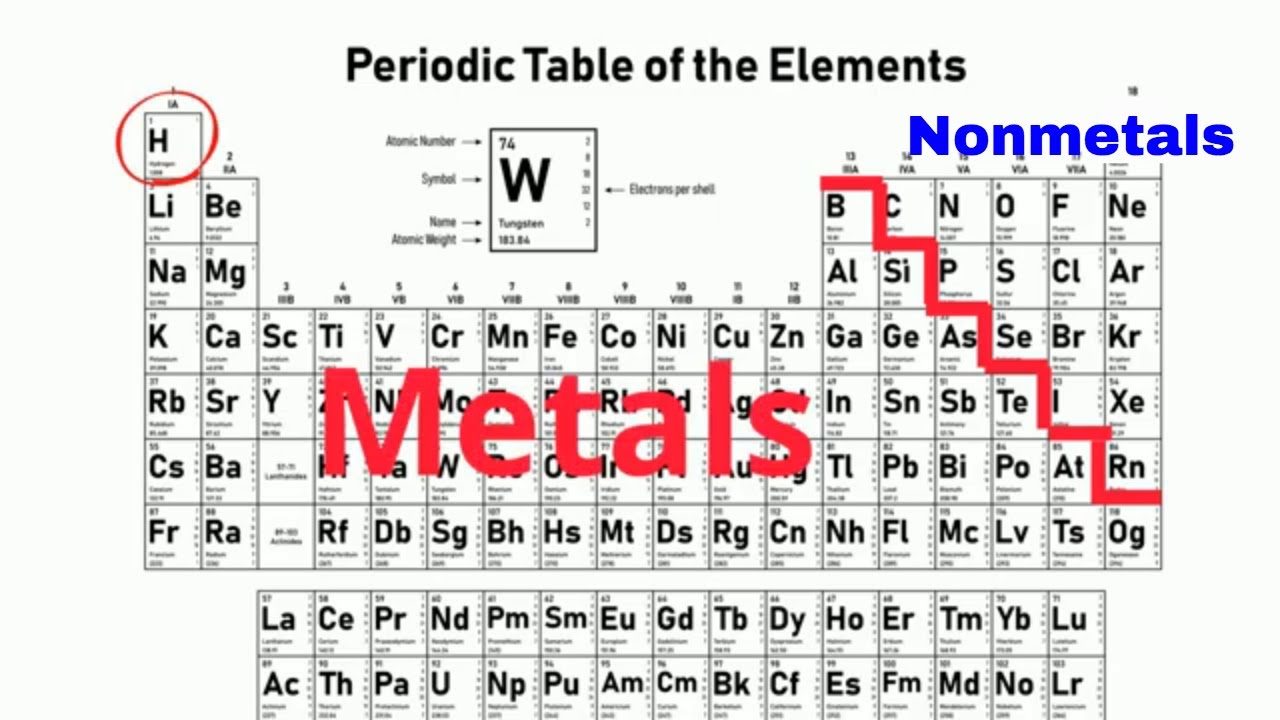
What are the metalloids on the periodic table. The metalloids also known as semi-metals are placed between metals and non-metals in the periodic table of elements. There are seven elements that are classified as metalloids and placed in Group 13 14 15 16 and 17. They are found in a stair step line that helps differentiate metals from non-metals in this element table.
Recognition status as metalloids of some elements in the p-block of the periodic table. Percentages are median appearance frequencies in the lists of metalloids. The staircase-shaped line is a typical example of the arbitrary metalnonmetal dividing line found on some periodic tables.
Location on the Periodic Table The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table. Because these elements have intermediate properties its sort of a judgment call as to whether a particular element is a metalloid or should be assigned to one of the other groups. Most of the elements in the periodic table are either a metal or a nonmetal but some have shared properties of both metals and nonmetals and are called the metalloids.
At the point where the. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups.
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table.
Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. The elements which are found in the step-like line between metals and nonmetals of the periodic table are known as the metalloids. Antimony Sb germanium Ge silicon Si arsenic As tellurium Te polonium Po boron B and astatine At.
What is the definition of the term metalloid. The elements most often regarded as metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony and tellurium. Wikipedia categorises these six as metalloids.
Other sources may subtract from this list or add a varying number of other elements. In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals.
A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the left-hand side of the period. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids.
They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. Recognition status as metalloids of some elements in the p-block of the periodic table.
Percentages are median appearance frequencies in the lists of metalloids. The staircase-shaped line is a typical example of the arbitrary metalnonmetal dividing line found on some periodic tables. The metalloids are a group of elements in the periodic table.
They are located to the right of the post-transition metals and to the left of the non-metals. Metalloids have some properties in common with metals and some in common with non-metals. What elements are metalloids.
Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. These elements are called metalloids or. Chemistry The Periodic Table Metalloids.
Why are metalloids unique. Metalloids are unique because they have properties of both metals and non-metals. For example boron acts as a nonmetal when it reacts with sodium but it acts as a metal when it reacts with fluorine.
Silicon has a metallic lustre but it is a poor conductor and. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine.
The noble gases are almost completely inert. 12176 amu Number of ProtonsElectrons. 51 Number of Neutrons.
71 Date of Discovery. Known to the ancients Discoverer. Hardens lead plastics chemicals Classification.