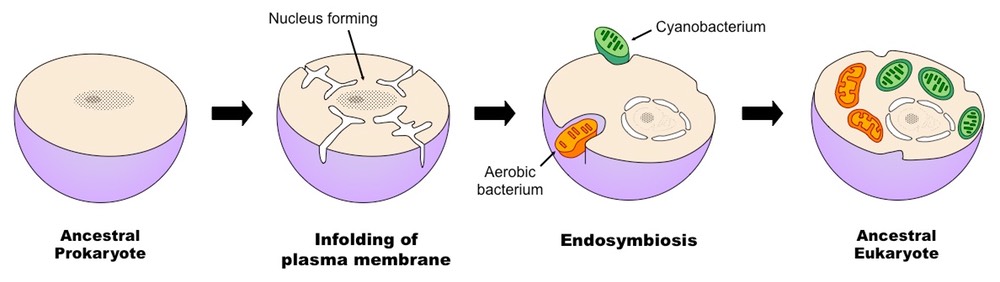
According to this theory the first eukaryotes were probably some Protozoans eg. An endosymbiont is a cell which lives inside another cell with mutual benefit Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis The engulfed prokaryotic cell remained undigested as it contributed new functionality to the engulfing cell eg.
Endosymbiotic theory or endosymbiosis is a hypothesized process that explains the origin of some organelles in eukaryotic cells.
What is the endosymbiotic theory. Endosymbiotic Theory Definition Endosymbiotic theory is the unified and widely accepted theory of how organelles arose in organisms differing prokaryotic organisms from eukaryotic organisms. In endosymbiotic theory consistent with general evolutionary theory all organisms arose from a single common ancestor. The endosymbiotic theory is the accepted mechanism for how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
It involves a cooperative relationship between two cells which allow both to surviveand eventually led to the development of all life on Earth. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one.
All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. Evolutionary biology A theory suggesting that the organelle s such as mitochondria and chloroplast s within the eukaryotic cell came about as a result of the early endosymbiosis between prokaryotic endosymbionts and eukaryotic host cell.
Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells. The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
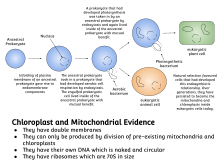
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the same size as prokaryotic cells and divide by binary fission. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA which is circular not linear. Endosymbiotic theory holds that chloroplasts and mitochondria came about through the evolution of blue-green algae and bacteria through endocytosis.
Endocytosis occurs when a substance passes into a cell through the cells membrane and then the cell plasma fuses together to keep the material inside forming an intracellular vesicle. The endosymbiotic theory is the explanation for mitochondria that gives energy to the cells and also for chloroplasts which is the origin of all of the plants. It also is the reason that is given for some of the other organelles of the cell.
Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis.
The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates to t. What is the Endosymbiotic theory. Endosymbiotic theory stats that the modern eukaryotic cells mitochondria evolved in steps through inter-cooperation into cells from a nuclear line of descendants of chemoorganotrophic and phototrophic symbionts.
Explore the endosymbiotic theory with the Amoeba Sisters. This theory explains the development of the eukaryote cell from prokaryote cell symbiosis. An endosymbiont is a cell which lives inside another cell with mutual benefit Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis The engulfed prokaryotic cell remained undigested as it contributed new functionality to the engulfing cell eg.
Endosymbiotic-theory meaning A theory stating that the eukaryotes evolved through a process whereby different types of free-living prokaryotes became incorporated inside larger prokaryotic cells and eventually developed into mitochondria chloroplasts and possibly other organelles. The endosymbiotic theory describes and explains the process of the creation of the cells of all animal and vegetable life. It has the cell biology of the 20th century revolutionized like no other concept.
It founds hardly a feature of public perception as a biological theory. An endosymbiotic relationship on the other hand is when a smaller organism lives within a host. Expanding on this it was hypothesised that an archea engulfed a bacterium into its cytoplasm through endocytosis and due to the transferring of genes to from the host it resulted in a nuclear genome.
The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles eg. Mitochondria chloroplast in todays eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes. According to this theory the first eukaryotes were probably some Protozoans eg.
Amoeba that were unicellular and intook nutrients in the food vacuole through the process of phagocytosis. Endosymbiotic theory or endosymbiosis is a hypothesized process that explains the origin of some organelles in eukaryotic cells. This theory describes the mechanism by which mitochondria and chloroplasts entered eukaryotic cells.
These two organelles have their own DNA.