When should you use the impulse momentum change equation. The impulse experienced by an object is always equal to the change in its momentum.
Consider a body of mass m moving with an initial velocity v i Suppose an external force F acts upon it for time t after which velocity becomes v f and acceleration are produced in the body.
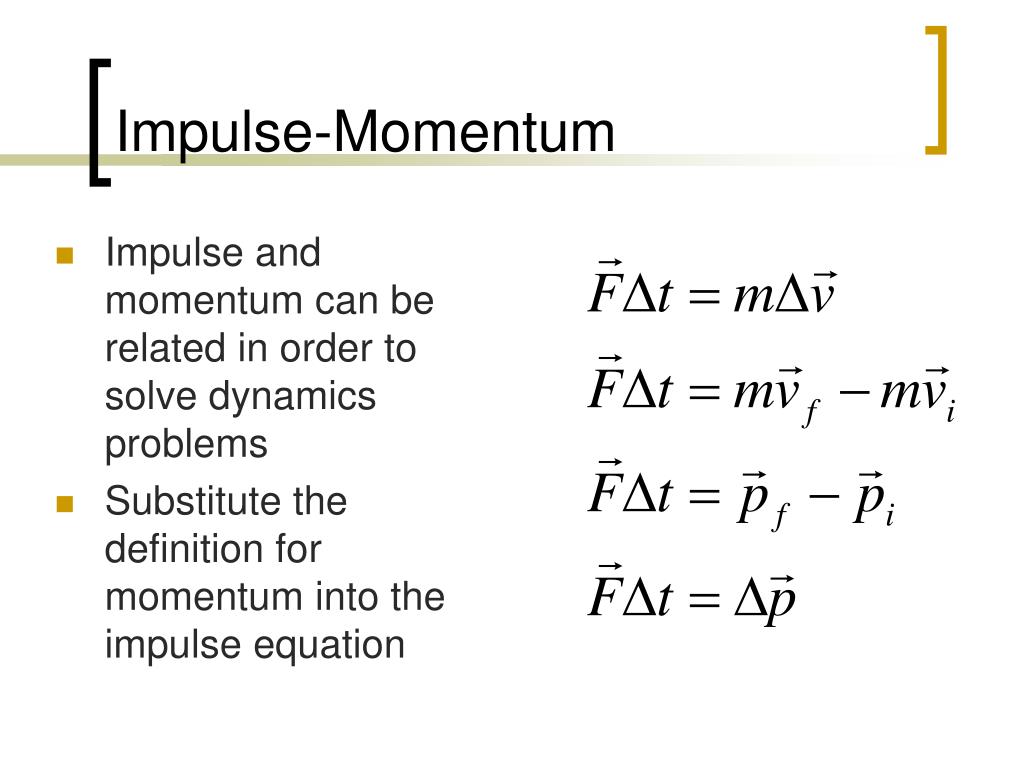
What is the relationship between impulse and momentum. A force acting upon an object for some duration of time results in an impulse. The quantity impulse is calculated by multiplying force and time. Impulses cause objects to change their momentum.
And finally the impulse an object experiences is equal to the momentum change that results from it. This equivalence is known as the impulse-momentum theorem. Because of the impulse-momentum theorem we can make a direct connection between how a force acts on an object over time and the motion of the object.
One of the reasons why impulse is important and useful is that in the real world forces are often not constant. Equation representing relationship between impulse and momentum The Greek letter delta means change in and we read this equation as force times the time interval equals change in mass times. An important relationship between impulse and momentum derived from Newtons second law which shows that the impulse of force is equal to the change in momentum that it produces.
What is the relationship between impulse and momentum. It is simple - and extremely powerful. The impulse-momentum equation says.
Or sometimes Impulse Change in Momentum. Since impulse is only change in momentum it has same units as that of momentum which is kg ms Impulse is also defined as force acting for duration upon a body Momentum of a moving body is the product of its mass and its velocity whereas impulse is change in momentum which is the product of mass and difference in velocities. Momentum is calculated as the product of mass and velocity while impulse is calculated as the integral of a force over a period of time for which it acts The main difference is in how they are calculated what they represent and what they inherently take into account.
Momentum is calculated by multiplying the mass and velocity together. Impulse is directly related to momentum because impulse is a term describing an objects change in momentum. In other words if an object changes speed then its momentum changes.
By definition this measurable quantity of momentum changing is the impulse of the object. What is ImpulseRelationship Between Impulse and MomentumHow to calculate impulsePhysicsExamplesAnimationIn this video you will learn about the concept. Describe the relationship between momentum and a force.
Newtons second law describes how the velocity is changed by a force acting on it. When should you use the impulse momentum change equation. When determining the new momentum or the new velocity of an object.
Impulse is defined as the change in momentum over time so it has the same units as momentum. An initial momentum mv1 changes to a final momentum mv2 with the application of a temporary and constant force N over a certain time interval after which the force ends and the velocity stops accelerating. The force multiplied by the time is known as the impulse and the mass multiplied by the velocity change is known as the change in momentum.
The impulse experienced by an object is always equal to the change in its momentum. In terms of equations this was expressed as This is known as the impulse-momentum change theorem. RelationshipBetweenImpulseandMomentum Wejustlearnedthat Thereforewhenyouapplyanimpulsetoanobjectieyou applyanetforceoveraperiodoftimeyouchangethe momentumoftheobject.
The SI unit of momentum is kgms-1 kilogram meter per second. It can also be expressed as newton second Ns. Relation between Force and Momentum.
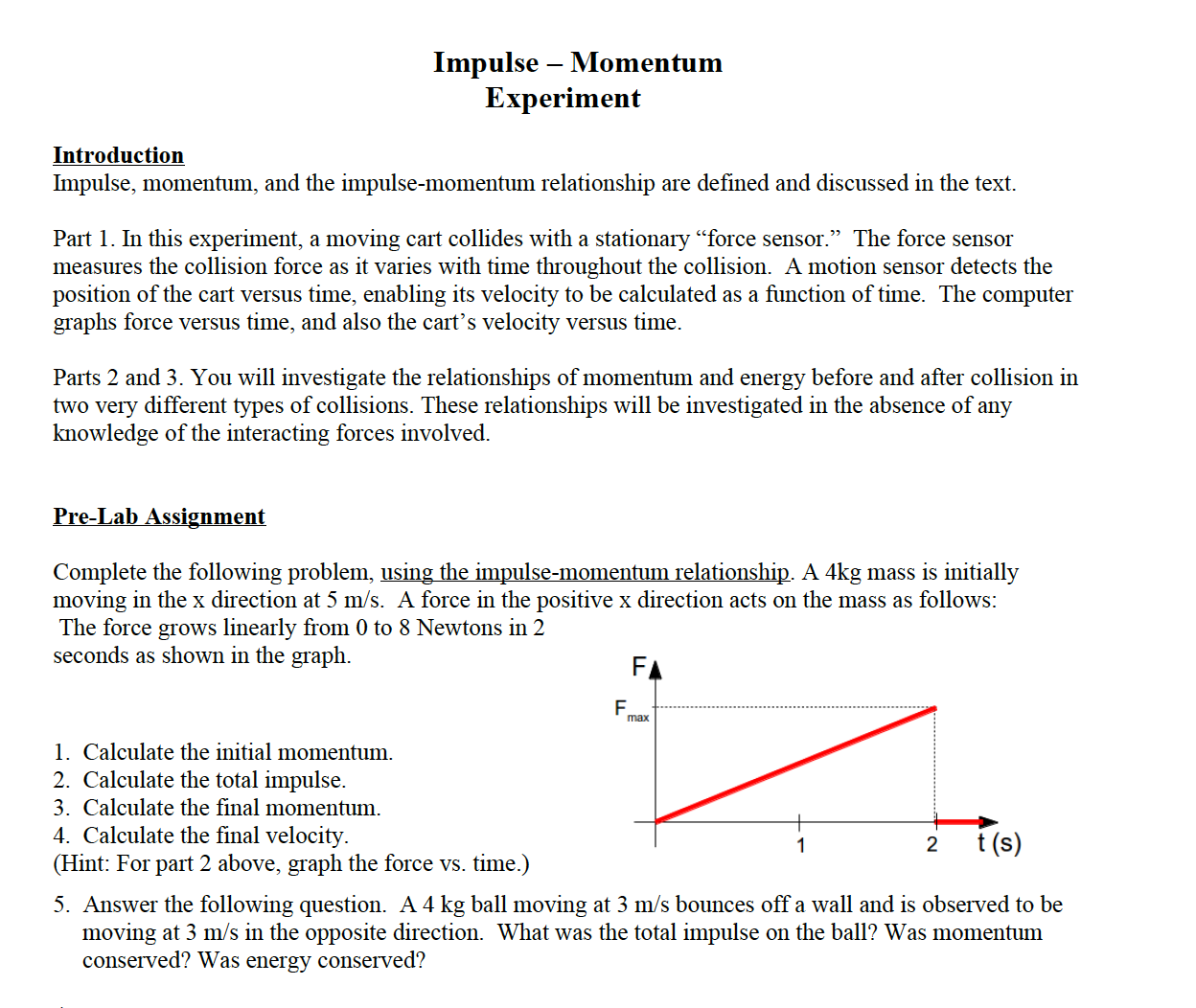
Consider a body of mass m moving with an initial velocity v i Suppose an external force F acts upon it for time t after which velocity becomes v f and acceleration are produced in the body. If Pi and Pf be the initial momentum and final momentum. Momentum kinetic energy and impulse can be used to analyse collisions between objects such as vehicles or balls.
Forces and the final velocity of objects can be determined. Impulse-momentum relationship a very useful form of Newtons 2nd Law. Impulse product of net force and the time over which the net force is applied ΣF.
T Impulse Change of Momentum. You will learn about the relationship between impulse and momentum and how to calculate impulse through a variety of examples. Newtons First Law of Motion.
Examples of the Effect of Force on.